Dental Implant Materials
Question 1. Classify different implant materials used in the field of dentistry. Write in short about titanium as an implant material.
Answer:
A dental implant is a material or device placed in and/ or on oral tissues to support an oral prosthesis.
Classification of Different Implant Materials Used in the Field of Dentistry:
1. Based on the materials used:
- Metals and alloys: It consists of titanium and its alloys, stainless steel, cobalt-chromium and molybdenum
- Ceramics and carbon implants: Made of carbon with stainless steel
- Polymers and composites: Polymethylmethacrylate and polytetrafluoroethylene.
Read And Learn More: Dental Materials Question And Answers
2. Based on biological response:
- Biotolerant: Such materials are not easily rejected when implanted in living tissue and are surrounded by fibrous layer in the form of a capsule, for example:
- Metals such as gold, cobalt–chromium alloy, stainless steel, zirconium, niobium
- Polymers like polyethylene, polyamide, polymethylmethacrylate, polyurethane
- Bioinert: These materials allow close apposition of bone over their surface causing contact osteogenesis. Examples are:
- Metals such as commercially pure titanium and titanium alloy
- Ceramics like aluminum oxide and zirconium oxide
- Bioactive: These materials allow the formation of bone onto their surface, but the exchange of ions along with host tissue causes the formation of the chemical bond at interface.
- Examples are: Ceramics like hydroxyapatite (HA), tricalcium phosphate, bioglass, fluorapatite, and carbon–silicon.
Titanium as Implant Material:
Titanium as implant material is most commonly and widely used. Titanium and its alloys are of the following types, i.e.
- Commercially pure titanium (CpTi)
- Titanium–6 aluminum–4 vanadium (Ti–6Al–4Va).
1. Commercially Pure Titanium:
Based on iron content commercially pure titanium is differentiated in four grades. It ranges from 0.2% to 0.5% from Grade 1 to Grade 4.
- Microstructure:
- It consists of two phases, i.e.
- Hexagonal close-packed, i.e. alpha phase
- Body centered cubic, i.e. beta phase.
- Properties: Titanium has the property of passivation on contact with either air or tissue fluid which decreases biocorrosion. Titanium is always covered by an external oxide layer, i.e. titanium oxide layer which is inert biologically and aids in osseointegration.
- Its thickness is 2 to 10 nm
- The modulus of elasticity of commercially pure titanium is fie times more than compact bone.
- Titanium is light in weight and its density is 4.51 gm/cm.
- The melting point of commercially pure titanium is 1668°C.
- It has excellent biocompatibility
- Commercially pure titanium contains oxygen and a minor amount of impurities such as nitrogen, carbon, hydrogen etc.
2. Titanium—6 Aluminum—4 Vanadium (Ti—6Al—4Va):
This is the alloy form of titanium.
Composition:
- Its composition is:
- 90% titanium
- 6% Aluminum
- 4% Vanadium
Properties:
- Its modulus of elasticity is 5 to 6 times of compact bone.
- It has the property of passivation on contact with air and tissue
flids which is 60% stronger than pure titanium.
Metal with Surface Coatings:
- The new implant design used in titanium is plasma sprayed or coated with thin layer of calcium phosphate ceramic or hydroxyapatite to produce bioactive surface which promotes bone growth. Her bond is chemical in nature as bone integrates with the coated surface.
- In this, a porous or rough titanium surface has been fabricated by plasma spraying in powder form of molten droplets at 1500°C temperature.
- Porous titanium surface from various fabrication methods
may increase the total surface area (up to several times), produce attachment by osteoformation, enhance by increasing ionic interactions, and introduce a dual physical and chemical anchor system, and increase the load-bearing capability from 25% to 30%. - The coatings have been applied to a wide range of endosteal and subperiosteal dental implants with the overall intent of improving implant surface biocompatibility profiles and implant longevities.
Question 2. Write a short note on a dental implant.
Answer:
“A dental implant is a material or device placed in and/or on oral tissues to support an oral prosthesis”. Glossary of prosthodontics terminology (GPT) 8th edition. Dr Leonard Linkow in 1952 place first dental implant and is recognized as the Father of Modern Implant dentistry.
Characteristics of Dental Implant:
- The implant should be made by highly biocompatible material such as titanium.
- It should be sterile.
- The implant is inserted by atraumatic surgical technique.
- The implant should have primary stability.
- The implant should have adequate loading at the time of healing period.
- The implant should have surface configurations which lead to oleophilic attraction.
- Implant should consist of two parts, i.e. one which favors bio adhesion and another which favors non-adhesion.
Parts of an Implant:
- Abutment: Part of the implant which supports the crown and provides retention to it. The abutment looks like a prepared tooth. It is attached to the body of an implant.
- Implant body/future: At the time of implant surgery, the implant body is placed in the bone. The function of the implant body/future is to receive the abutment.
- Healing screw: It should be placed over the implant body after first stage of surgery, this facilitates suturing of tissues and prevent the growth of tissues over the edge of an implant.
- Healing cap: It should be placed over the implant body and protrude outside tissues in oral cavity. Healing caps lead to the maintenance of tissue contour around the implants.
Advantages of Implant:
- Implants prevent the cutting of naturally healthy teeth for receiving the field prosthesis.
- They preserve the bone and decrease bone resorption.
- Implants decrease load over remaining natural teeth since they offer individual support.
- Implants improve efficiency in chewing and speaking as compared to complete denture wearers.
Disadvantages of Implant:
- The patient has to undergo a surgical procedure.
- To enable healing before the prosthesis waiting period of 3 to 4 months is required.
- Implants are costly.
Indications of Implant:
- In cases where there is loss of one or more natural teeth.
- In cases where good quantity and quality of bone is present around the edentulous area.
- In cases where the patient does not want a reduction of the natural tooth for field prosthesis.
- For providing support to overdentures.
- In implant-supported maxillofacial prosthesis.
Contraindications of Implant:
- In edentulous cases where bone quality is not appropriate.
- In cases with bruxism.
- In patients on steroid therapy.
- Patients with bleeding disorders.
- Patients with immunodeficient conditions.
Question 3. Write a short note on the classification and materials used in implants.
Answer:
Classifiation of Implants:
1. Based on the Materials Used:
- Metals and alloys: It consists of titanium and its alloys, stainless steel, cobalt-chromium, and molybdenum
- Ceramics and carbon implants: Made of carbon with stainless steel
- Polymers and composites: Polymethylmethacrylate and polytetrafluoroethylene.
2. Based on biological response:
- Biotolerant: Such materials are not easily rejected when implanted in living tissue and are surrounded by firous layer in the form of a capsule, for example
- Metals such as gold, cobalt–chromium alloy, stainless steel, zirconium, niobium
- Polymers like polyethylene, polyamide, polymethylmethacrylate, and polyurethane.
- Bioinert: These materials allow close apposition of bone over their surface causing contact osteogenesis. Examples are:
- Metals such as commercially pure titanium and titanium alloy
- Ceramics like aluminum oxide and zirconium oxide
- Bioactive: These materials allow the formation of bone on their surface, but the exchange of ion along with host tissue causes the formation of the chemical bond at interface.
- Examples are: Ceramics like HA, b-tricalcium phosphate, bioglass, fluorapatite, and carbon–silicon.
3. Based on Histology:
- Osseointegrated
- Non-osseointegrated.
4. Based on the Design of the Implant:
- Endosteal implants: They are placed in the alveolar or basal bone of the maxilla and mandible, and they transect only one cortical plate, for example, Blade implants and ramus frame implants.
- Subperiosteal implant: It consists of an implant substructure which is a custom-cast frame placed directly over the bony cortex just below the periosteum.
- Transosteal implant: It penetrates both cortical plates, for example, the Transmandibular implant, and mandibular staple implant.
5. Based on Macroscopic Design:
- Threaded or threadless
- Cylindrical or conical
- Hollow or solid.
6. Based on surface treatment:
- Titanium plasma-sprayed
- Aluminum oxide coated
- Hydroxyapatite coated
- Machined
- Blasted or etched with biomaterials
- Electropolished.
Materials used in Implants:
- Metals: Stainless steel, cobalt-chromium-molybdenum, titanium alloys and surface coated titanium
- Ceramics: Hydroxyapatite, bioglass, aluminum oxide
- Polymers and composites
- Others: Gold, tantalum, carbon, etc.
- Stainless Steel: Austentic steel is used as implant material. It has high strength and ductility so is rarely used.
- Titanium: Titanium as implant material is most commonly and widely used. Titanium and its alloys are of the following types, i.e.
- Commercially pure titanium (CpTi)
- Titanium–6 Aluminum–4 Vanadium (Ti–6Al–4Va).
1. Commercially Pure Titanium: Based on iron content commercially pure titanium is differentiated in four grades. It ranges from 0.2% to 0.5% from Grade 1 to Grade 4
- Microstructure: It consists of two phases, i.e.
- Hexagonal close-packed, i.e. alpha phase
- Body-centred-cubic, i.e. beta phase.
- Properties: Titanium has the property of passivation on contact with either air or tissue flid which decreases biocorrosion. Titanium is always covered by an external oxide layer, i.e. titanium oxide layer which is inert biologically and aids in osseointegration.
- Its thickness is 2 to 10 nm
- The modulus of elasticity of commercially pure titanium is five times more than compact bone.
- Titanium is light in weight and its density is 4.51 g/cm.
- The melting point of commercially pure titanium is 1668°C.
- It has excellent biocompatibility.
- Commercially pure titanium contains oxygen and a minor amount of impurities such as nitrogen, carbon, hydrogen, etc.
2. Titanium–6 Aluminum–4 Vanadium (Ti–6Al–4Va): This is the alloy form of titanium.
- Composition: Its composition is:
- 90% Titanium
- 6% Aluminum
- 4% Vanadium.
- Properties:
- Its modulus of elasticity is 5 to 6 times of compact bone.
- It has the property of passivation on contact with air and tissue flids which is 60% stronger than pure titanium.
- Ceramics: They can be bioactive or bioinert. They are of limited use because of low tensile strength and ductility. They are used as surface coats on titanium implants.
- Polymers and Composites: They are fabricated in porous and solid forms for tissue attachments and replacement augmentation. In some of the implants, they are mainly used within the implants as connectors for stress distribution.
- Other Materials: Gold, tantalum, carbon, etc. materials were used in the past. Recently zirconia and tungsten are used. Carbon was recently used as coatings for metallic and ceramic devices.
Question 4. Write a short note on the classification of dental implants.
Or
Write a short note on the type of implants.
Answer:
Classifiation of Implants:
1. Based on the Materials Used:
- Metals and alloys: It consists of titanium and its alloys, stainless steel, cobalt-chromium, and molybdenum
- Ceramics and carbon implants: Made of carbon with stainless steel
- Polymers and composites: Polymethylmethacrylate and polytetrafluoroethylene.
2. Based on Biological Response:
- Biotolerant: Such materials are not easily rejected when implanted in living tissue and are surrounded by a fibrous layer in the form of a capsule. For example,
- Metals such as gold, cobalt–chromium alloy, stainless Steel, zirconium, niobium
- Polymers like polyethylene, polyamide, Polymethylmethacrylate,
- Bioinert: These materials allow close apposition of bone over their surface causing contact osteogenesis. Examples are:
- Metals such as commercially pure titanium and titanium alloy
- Ceramics like aluminum oxide and zirconium oxide
- Bioactive: These materials allow the formation of bone onto their surface, but the exchange of ions along with host tissue causes the formation of the chemical bond at the interface. ,
- Examples are: Ceramics like HA, tricalcium phosphate, bioglass, fluorapatite, and carbon–silicon.
3. Based on Histology:
- Osseointegrated
- Non-osseointegrated.
4. Based on the Design of the Implant:
- Endosteal implants: They are placed in the alveolar or basal bone of the maxilla and mandible and they transect only one cortical plate, For example, Blade implants and ramus frame implants.
- Subperiosteal implant: It consists of an implant substructure which is a custom-cast frame placed directly over the bony cortex just below the periosteum.
- Transosteal implant: It penetrates both cortical plates, For example, the Transmandibular implant, and mandibular staple implant.
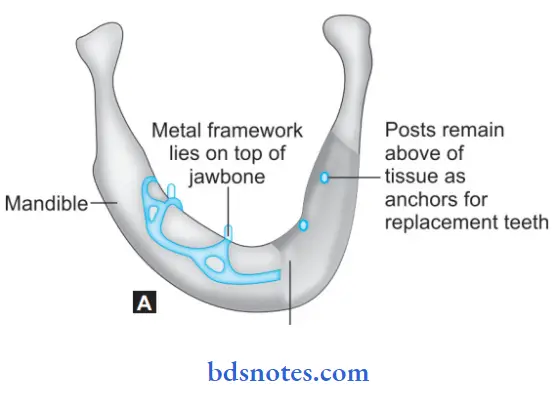
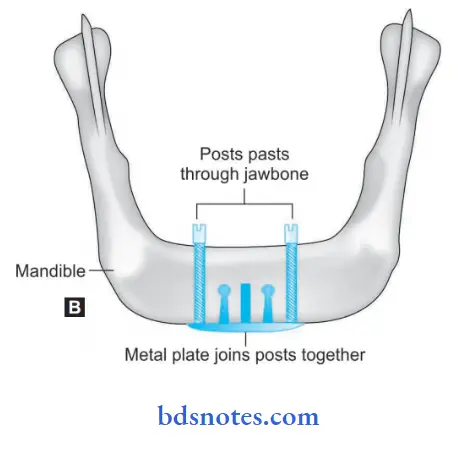
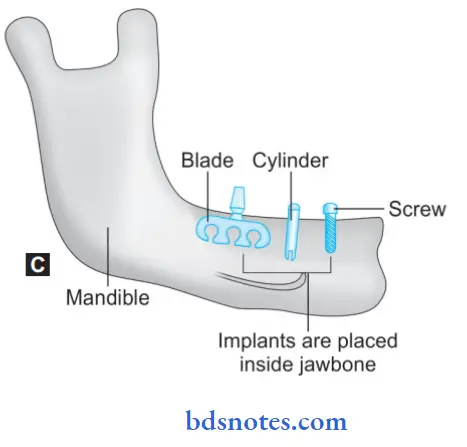
5. Based on Macroscopic Design:
- Threaded or threadless
- Cylindrical or conical
- Hollow or solid
6. Based on surface treatment:
- Titanium plasma-sprayed
- Aluminum oxide coated
- Hydroxyapatite coated
- Machined
- Blasted or etched with biomaterials
- Electropolished.
Question 5. Write a short note on implant biomaterial.
Or
Write a short note on biomaterials used in implants.
Answer:
Biomaterial is defined as a non-viable material used in a medicinal device intended to interact with biological systems.
Biomaterials, regardless of use, fall into four general categories:
- Metals and metallic alloys
- Ceramics
- Synthetic polymers
- Natural materials
Metals and metal alloys that utilize oral implants include titanium, tantalum, and alloy of Ti-Al-Va, Co-Cr-Mb, and Fe-Cr-Ni.
These materials are generally selected on the basis of their overall strength properties:
- Bioinert materials allow close approximation of bone on their surface leading to contact osteogenesis.
- These materials allow the formation of new bone on their surface and ion exchange with the tissues leads to the formation of a chemical bonding along the interface bonding osteogenesis.
- Biotolerant are those that are not necessarily rejected when implanted into living tissue.
- They are recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 (rhBMP-2) which induces de novo bone formation.
- Biomimetics are tissue-integrated engineered materials designed to mimic specific biologic processes and help optimize the healing/regenerative response of the host microenvironment.
- Bioinert and bioactive materials are also called osteoconductive, meaning that they can act as scaffolds allowing bone growth on their surface.
Titanium and its Alloys:
Titanium as implant material is most commonly and widely used. It has a good record of being used successfully as an implant material and this success with titanium implants is credited to its excellent biocompatibility due to the formation of a stable oxide layer on its surface.
Titanium and its alloys are of the following types, i.e.
- Commercially pure titanium (Cp–Ti)
- Titanium–6 Aluminum–4 Vanadium (Ti–6Al–4Va)
Commercially Pure Titanium:
- The commercially pure titanium (cpTi) is classified into 4 grades which differ in oxygen content.
- Grade 4 is having the most (0.4%) and grade 1 is the least(0.18%) oxygen content.
- The mechanical differences that exist between the different grades of commercially pure titanium is primarily because of the contaminants that are present in minute quantities.
- Iron is added for corrosion resistance and aluminum is added for increased strength and decreased density, while vanadium acts as an aluminum scavenger to prevent corrosion.
- The hexagonal close-packed crystal lattice of Ti is called the α-Ti (α-phase). On heating it at 883°C phase transformation occurs from hexagonal close-packed to body-centered cubic lattce or β- phase
- Ti is reactive as it forms spontaneously a dense oxide fim at its surface.
- Ti is a dimorphic metal, i.e. below 882.5°C it exists as α-phase and above this temperature, it changes from α- phase to β-phase.
- Because of the high passivity, controlled thickness, rapid formation, ability to repair itself instantaneously if damaged, resistance to chemical attack, catalytic activity for a number of chemical reactions, and modulus of elasticity compatible with that of bone o, Ti is the material of choice for intraosseous applications.
Disadvantages its Alloys:
There is an esthetic issue due to the gray color of the titanium and this is more pronounced when the soft tissue situation is not optimal and the dark color shines through the thin mucosa.
Titanium—6 Aluminum—4 Vanadium (Ti—6Al—4Va):
- This is the alloy form of titanium.
- Titanium reacts with several other elements, For example, Silver, Al, Ar, Cu, Fe, Ur, Va, and Zn to form alloys.
- Titanium alloys exist in three forms, i.e. alpha, beta, and α-β.
- These types originate when pure titanium is heated with elements Al, and Va in certain concentrations and cooled, these types originate.
- These added elements play like phase-condition stabilizers.
- Aluminum is an alpha-phase condition stabilizer and it also increases the strength and decreases the weight of the alloy.
- Vanadium acts as a beta-phase stabilizer.
- The temperature at which α-to β transformation occurs changes to a range of temperatures as Al or Va is added to Ti.
- Both α and β forms exist in this range.
- Temperatures to which the desired form is present can be obtained by quenching the alloy at room temperature. To increase the strength, these alloys may be heat treated.
- The alloys most commonly used for dental implants are of the alpha-beta variety. The most common contains 6% Al and 4% Va. (Ti 6 Al 4V)
Iron-Chromium-Nickel Based Alloys: Stainless Steel:
Composition of Stainless Steel:
- 70% iron which is the main constituent
- 18% chromium provides corrosion resistance
- 8% nickel stabilizes the austenitic structure
The alloy is used in wrought and heat-treated conditions which results in high strength and ductility. Passivation is required to maximize biocorrosion resistance. Currently, they are rarely used.
Advantages of Stainless Steel:
- It is corrosion resistance
- It has increased ductility.
Disadvantages of Stainless Steel:
- It is vulnerable to crevice and pitting corrosion
- It is contraindicated in patients allergic to nickel
Ceramics of Stainless Steel:
- Ceramics are inorganic, nonmetallic, and nonpolymeric materials that are either bioactive or bioinert (osteoconductive). Ceramic implants get manufactured by compaction and sintering at high temperatures.
- Bioinert ceramics are used in various implants, i.e. root form, endosteal, plate form, and pin type dental implants.
- Bioactive ceramics are applied to titanium and cobalt alloy substrates by plasma spraying. Plasma spraying provides roughened, biologically acceptable surface for bone growth and ensures anchorage in the jaw. Particles are small-sized crystalline hydroxyapatite ceramics.
Polymers of Stainless Steel:
They are used for manufacturing superstructures. They mainly act as shock absorbers to the load-bearing implants. They are fabricated in porous and solid forms for tissue attachments and replacement augmentation.
Natural Materials of Stainless Steel:
Gold, tantalum, carbon, etc. Materials were used in the past. Recently zirconia and tungsten are used. Titanium has replaced most of these materials. Carbon was recently used as coatings for metallic and ceramic devices. Root form or endosteal plate form, and pin-type dental implants are generally made from high ceramics from aluminum, titanium, and zirconium oxides. The compressive, tensile, and bending strengths exceed the strength of compact bone by 3 to 5 times. These properties combined with high moduli of elasticity and especially with fatigue and fracture strength have resulted in specialized design requirements for this class of biomaterials.
Question 6. Write a short note on materials used in implants.
Or
Write a short answer on dental implant materials.
Answer:
Materials used in implants are:
- Metals: Stainless steel, cobalt-chromium-molybdenum, titanium and alloys and surface-coated titanium
- Ceramics: Hydroxyapatite, bioglass, aluminum oxide
- Polymers and composites
- Other: Gold, tantalum, carbon, etc.
- Stainless Steel: Austentic steel is used as implant material. It has high strength and ductility so is rarely used.
- Ceramics: They can be bioactive or bioinert. They are of limited use because of low tensile strength and ductility. They are used as surface coats on titanium implants.
- Polymers and Composites: They are fabricated in porous and solid forms for tissue attachments and replacement augmentation. In some of the implants, they are mainly used within the implants as connectors for stress distribution.

Leave a Reply