Dental Anatomy
Question 1. Write briefly about different tooth numbering systems.
(or)
FDI system of dental nomenclature.
Answer:
It is necessary to substitute the lengthy names of the individual teeth with some symbol.
- Thus, various numbering teeth by some symbol were introduced to designate individual teeth by a number or alphabetical letter.
1. Zsigmondy/palmer system:
- It was introduced by Adolph Zsigmondy of Vienna in 1861 for permanent dentition and modified for primary dentition in 1874.
Read And Learn More: BDS Previous Examination Question And Answers
For permanent dentition:
- As per this system, the oral cavity is divided into four quadrants and each permanent tooth has a specific number.
- Numbering progresses posteriorly from the midline.
- The central incisor was designated as 1 ending up with 8 for the third molar.
87654321 & 12345678 \\
\hline 87654321 & 12345678
\end{array}\)
For primary dentition:
- The deciduous central incisors are designated A & progress posteriorly up to the 2nd deciduous molar alphabetically designated E.
\text { EDCBA } & \text { ABCDE } \\
\hline \text { EDCBA } & \text { ABCDE }
\end{array}\)
2. Universal system:
For permanent dentition:
- In this system, the numbering starts from the right maxillary 3rd molar designated 1 to 16 designated to the left maxillary 3rd molar.
- Then beginning with the mandibular left 3rd molar, the teeth are numbered 17 to 32.
12345678 & 910111213141516 \\
\hline 3231302928272625 & 2423222120191817
\end{array}\)
For primary dentition:
- Alphabets are used starting from A-J for maxillary left 2nd molar.
- Then beginning with the mandibular left 2nd molar, the teeth are named K to T.
\text { ABCED } & \text { FGH I J } \\
\hline \text { TSRQP } & \text { ONMLK }
\end{array}\)
3. FDI numbering system:
- It is a two-digit system proposed by the federation dentaire international (FDI)
For permanent dentition:
- The first digit indicates the quadrant and is numbered from 1 to 4.
- The second digit indicates the tooth number starting from the central incisor as 1 to the 3rd molar as 8.
Thus,
For primary dentition:
\(\begin{array}{l|l}1817161514131211 & 2122232425262728 \\
\hline 4847464544434241 & 3132333435363738
\end{array}\)
- The first digit indicating quadrant is numbered from 5 to 8.
- The second digit is numbered from 1 to 5 from the central incisor to 2nd molar
5554535251 & 6162636465 \\
\hline 8584838281 & 7172737475
\end{array}\)
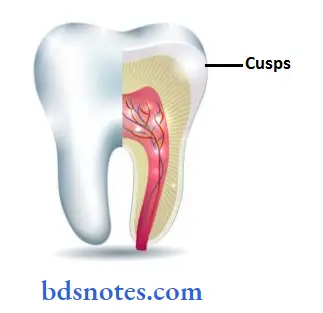
Question 2. CUSP.
Answer:
- It is an elevation or mound on the crown portion of a tooth making up a divisional part of the occlusal surface.
- It is an integral part of the occlusal surface.
- Generally, posterior teeth will have cusps.
- Different sets of teeth have different numbers of cusps.
- Example: Mandibular 1st permanent molar has 5 cusps.
- A small cusp, for example, cusps of clarabella present over permanent maxillary first molar is called caplet.
Function:
- Shearing & tearing of food substances.
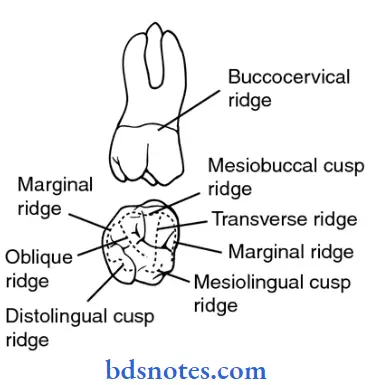
Question 3. Ridge.
Answer:
- It is any linear elevation on the surface of a tooth. It is named according to its location.
1. Marginal ridge:
- They are rounded borders of the enamel forming mesial and distal margins of the occlusal surfaces of posterior teeth and lingual surfaces of certain anterior teeth.
2. Traingular ridge:
- It is a ridge descending from the cusp tip of the premolars and molars towards the central part of the occlusal surface.
3. Oblique ridge:
- It crosses the occlusal surfaces of maxillary molars obliquely.
- It is formed by the union of the triangular ridge of the distobuccal cusp and the distal cusp ridge of the mesiolingual cusp.
4. Transverse ridge:
- It is formed by buccal and lingual triangular ridges.
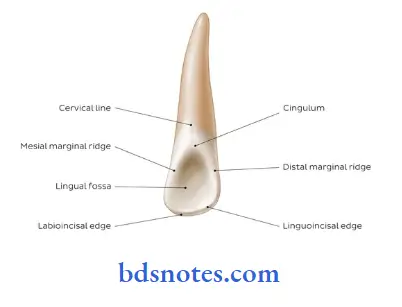
Question 4. Fossa.
Answer:
- It is an irregular depression or concavity found on the tooth surface.
Depending on their locations, they are named as:
- Lingual fossa – on the lingual surface of incisor.
- Central fossa – On the occlusal surface of molars.
- Triangular fossa – On occlusal surfaces of molars & premolars mesial or distal to the marginal ridges.
- Sometimes found on the lingual surfaces of maxillary incisors at the edge of the lingual fossae.
Question 5. Sulcus.
Answer:
- It is a long depression or valley over the occlusal surfaces of the posterior teeth between the ridges and cusps.
- The inclines of the valley meet at an angle.
- It has a development groove at the junction of its incline.
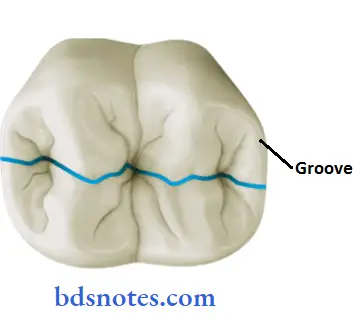
Question 6. Grooves.
Answer:
- They are development faults, clefts, or shallow grooves usually found on the occlusal or buccal& lingual surfaces of posterior teeth.
1. Development groove:
- A groove separates the primary parts of the crown or root.
2. Supplemental groove:
- It is a shallow linear depression on the tooth surface, supplemental to the developmental groove.
3. Buccal and lingual grooves:
- Found on the buccal and lingual surfaces of posterior teeth.
Appearance:
- They may be
- Shallow and wide
- Deep and narrow
Function:
- Play an important role in the initiation of tooth decay.
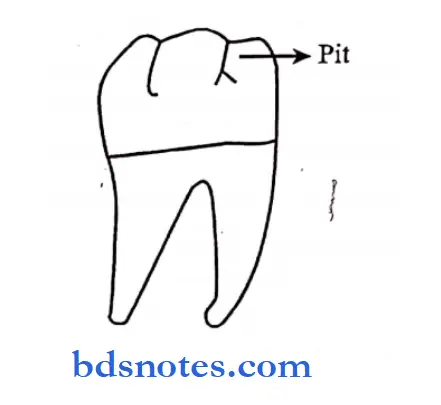
Question 7. Pits.
Answer:
- These are small or pin-point deep depressions in enamel, sometimes in dentin.
Site:
- At the junction of developmental grooves or at the terminals of those grooves.
- The central pit is located in the central fossa. Fossa of molars where developmental grooves join.
Significance:
- They act as areas for the initiation of dental carries.
Question 8. Mamelons.
Answer:
- It is any one of the three rounded protuberances found on the incisal ridges of newly erupted incisor teeth.
Significance:
- It represents a primary section of the formation in the development of the crown.
Fate:
- They are worn out with usage.
Variation:
- They may be missing by birth as in the case of congenital syphilis.

Question 9. Tubercle and cingulum.
Answer:
Tubercle:
- It is a smaller elevation on some portion of the crown produced by an extra formation of enamel.
Cingulum:
- It is the lingual lobe of an anterior tooth.
- It makes up the bulk of the cervical third of the lingual surface.
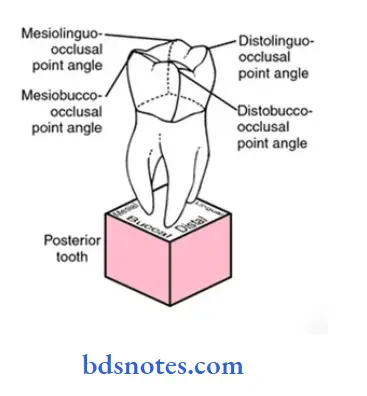
Question 10. Line angle and point angle.
Answer:
Line angle:
- It is formed by the junction of two surfaces and is named after the two surfaces forming this angle.
- The line angles in the anterior teeth are
- Mesiolabial, distolabial
- Mesiolingual, distolingual
- Labioincisal, linguoincisal.
- Line angles for posterior teeth are
-
- Mesiobuccal, distobuccal
- Mesiolingual, distolingual
- Mesio-occlusal, distoocclusal
- Bucco-occlusal, linguo-occlusal.
Point angle:
- It is formed by the junction of three surfaces and is named after the surfaces forming it.
- The point angles of anterior teeth are.
- Mesiobuccoocclusal
- Distobuccooclusal
- Mesiolinguoocclusal
- Distolinguoocclusal
Question 11. Crown.
Answer:
- Each tooth is made up of a crown and root.
- The crown is covered by enamel
- The junction between the crown and root is called Cemento Enamel Junction (CEJ) or cervical line.
- The main bulk of the crown is made up of dentin.
- It also contains a pulp chamber.
- It has
- An incisal edge in incisors
- One cusp in canine
- Two/more cusps in premolars and molars.
- It is never covered by bone tissue after it is fully erupted but is partly covered by soft tissue called gingiva.
Question 12. Dental formula.
Answer:
- The denomination of each tooth is represented by the initial letter in its name.
- I-incisors, C-canine, P-premolar, M-molar.
- Each letter is followed by a horizontal line and the number of each type of tooth is placed above the line for maxilla and below the line for mandible.
- The formula includes one side only.
- The formula for deciduous teeth is.
- The formula for permanent teeth is
[latex]\mathrm{I} \frac{2}{2} \mathrm{C} \frac{1}{1} \mathrm{P} \frac{2}{2} \mathrm{M} \frac{3}{3}=16\)
Question 13. Name tooth numbering systems.
Answer:
- Zsigmondy/plamer system
- Universal notation system.
- Two-digit system by FDI
Question 14. Define: fissure, ridge
Answer:
Fissure:
- Fissure is defined as the deep cleft between adjoining cusps
- It consists of an organic plug composed of reduced enamel epithelium, microorganisms forming dental plaque, and oral debris
- It has increased susceptibility to caries
Ridge:
- It is any linear elevation on the surface of the tooth
- It is named according to its location – buccal ridge, incisal ridge, marginal ridge.

Leave a Reply