Cysts Of Oral Cavity
Question.1.Classify cysts of oral cavity. Describe pathogenesis, histopathology and clinical features and roentgenographic appearance of dentigerous cyst.
Or
Define and classify cysts. Write in detail about dentigerous cyst.
Or
Classify odontogenic cyst. Describe pathogenesis, clinical radiological and histopathologic features of dentigerous cyst.
Or
Classify odontogenic cysts and describe clinical features, radiographic and histopathologic features of dentigerous cyst.
Or
Classifyodontogenic cyst. Describe pathogenesis, clinical, radiological features along with histopathology of dentigerous cyst.
Answer. Cyst is defined as “A pathological cavity having flid,semifluid or gaseous contents and which is not created by accumulation of pus.” — Kramer (1974)
Classification of Cyst of Oral Cavity by Mervin Shear
Cysts of the Jaws
- Epithelial:
- Developmental:
- Odontogenic:
- Gingival cyst of infants
- Odontogenic keratocyst (Neoplasm)
- Dentigerous cyst
- Eruption cyst
- Lateral periodontal cyst
- Gingival cyst of adults
- Botryoid odontogenic cyst
- Glandular odontogenic cyst
- Calcifying odontogenic cyst (neoplasm)
- Odontogenic:
- Developmental:
Read And Learn More: Oral Pathology Question And Answers
-
-
- Non-odontogenic:
- Naso palatine duct cyst
- Naso labial cyst
- Midpalatal raphe cyst of infants
- Median palatine, median alveolar
- Median mandibular cyst
- Globulo maxillary cyst
- Non-odontogenic:
- Inflammatory
- Radicular cyst, apical and lateral
- Residual cyst
- Paradental cyst and mandibular infected buccal cyst
Inflammatory collateral cyst
-
- Nonepithelial (pseudocysts)
- Solitary bone cyst
- Aneurysmal bone cyst
Cyst Associated With Maxillary Antrum
- Benign mucosal cyst of the maxillary antrum
- Post-operative maxillary cyst
Cyst of the Soft Tissues Of Mouth, Face And Neck
- Dermoid and epidermoid cyst
- Lymphoepithelial cyst (branchial cyst)
- Thyroglossal duct cyst
- Anterior medial lingual cyst (intra lingual cyst of foregut origin)
- Oral cyst with gastric or intestinal epithelium
- Cystic hygroma
- Nasopharyngeal cyst
- Thymic cyst
- Cyst of salivary glandsmucous extravasation cyst
- Mucous retention cyst, ranula, polycystic disease of the parotid.
- Parasitic cyst hydatid cyst, cysticercus cellulosae, trichinosis.
Classification of Odontogenic Cyst
WHO (2017) Classification of Odontogenic Cysts
- Odontogenic cysts of inflammatory origin
- Radicular cyst
- Inflammatory collateral cysts
- Odontogenic developmental cysts
- Dentigerous cyst
- Odontogenic keratocyst
- Lateral periodontal cyst and botryoid odontogenic cyst
- Gingival cysts
- Glandular odontogenic cyst
- Calcifying odontogenic cyst
- Orthokeratinized odontogenic cyst.
Dentigerous Cyst
- It is also called as follicular cyst or pericoronal cyst
- It is the odontogenic cyst that surrounds the crown of the impacted tooth.
Pathogenesis Of Dentigerous Cyst
- Intrafollicular theory: Dentigerous cyst is caused by flid accumulation between reduced enamel epithelium and enamel surface which result in a cyst in which crown is located within the lumen.
- Extrafollicular theory: Dentigerous cyst may arise by proliferation and cystic transformation of islands by odontogenic epithelium in connective tissue wall of dental follicle or even outside dental follicle and this transformed epithelium then unite with lining follicular epithelium forming cystic cavity around tooth crown.
Clinical Features Of Dentigerous Cyst
- It is usually found in the children.
- Most lesions are present in the 2nd and 3rd decades with male predilection.
- Most common site of the cyst are the mandibular and maxillary third molar and maxillary cuspid areas, since these are most commonly impacted teeth.
- Generally, it is painless but may be painful if it is infected.
- Dentigerous cyst has potential to become an aggressive
lesion with expansion of bone and subsequent facial asymmetry. - There is extreme displacement of teeth, severe root resorption of adjacent teeth and pain.
Histopathological Features Of Dentigerous Cyst
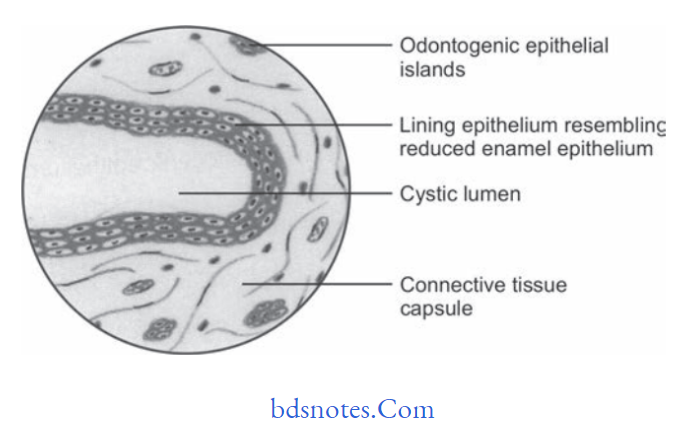
- The epithelial lining consists of two to four layers of flattened nonkeratinizing cells and the epithelium and connective tissue interface is flt.
- It is usually composed of thin connective tissue wall with a thin layer of stratifid squamous epithelium lining the lumen.
- Rete pegs formation is absent except in case of secondarily infected cyst.
- Connective tissue wall is frequently quite thickened and composed of very loose firous connective tissue.
- Inflammatory cells commonly infiltrate connective tissue
- It also shows Rushton bodies within the lining epithelium which are peculiar linear and often curved hyaline bodies.
- Content of cystic lumen is usually thin watery yellow flid and is occasionally blood tinged.
Roentgenographic/Radiological Features
- There is presence of well-defied radiolucency having hyperostotic borders.
- An unerupted tooth is also seen around the radiolucency
- Cyst is unilocular but at times it appears multilocular.
- Bony margins of the cyst are well defied as well as sharp.
- If infection persists margins are ill defied.
- Cyst can envelop the crown symmetrically, but it can expand laterally from the crown of tooth. Tooth can also be displaced away in any direction.
- Resorption of roots of adjacent teeth can also be seen.
- Floor of maxillary sinus gets displaced with the expansion of cyst.
Question.2.Classify cysts of jaw. Describe pathogenesis, histopathology and clinical features, and malignant potential of dentigerous cyst.
Answer.
Malignant potential of Dentigerous Cyst
- Malignant potential of the epithelium of dentigerous cysts to ameloblastoma, epidermoid carcinoma and mucoepidermoid carcinoma.
- Development of an ameloblastoma is from rest of odontogenic epithelium or from lining epithelium of cyst is known as mural ameloblastoma.
- Mucoepidermoid carcinoma is the malignancy of salivary gland. The mucoepidermoid carcinoma is usually associated with lining epithelium of dentigerous cyst or dentigerous cyst which consist of mucous secreting cell.
- Epidermoid carcinoma can also develop from dentigerous cyst from rest of odontogenic epithelium or lining of epithelium of cyst.
Question.3.Classify cysts of jaw. Describe pathogenesis, histopathology and clinical features of odontogenic keratocyst.
Or
Describe the pathogenesis, histopathology and clinical features of odontogenic keratocyst.
Or
Classify odontogenic cysts of oral cavity. Write about clinical features and histopathology of odontogenic keratocyst.
Or
Write in detail on odontogenic keratocyst.
Or
Classify odontogenic cysts of oral cavity describe clinical features and histopathology of keratocyst.
Or
Classify odontogenic cysts and describe the clincial and histopathological features of odontogenic keratocyst (OKC) in detail.
Or
Classify odontogenic cysts. Describe pathogenesis,clinical, radiological and histopathological features of odontogenic keratocyst.
Or
Classify odontogenic cysts. Discuss clinical features,radiological features and histopathology of odontogenic keratocyst.
Answer.
Odontogenic Keratocyst
Odontogenic keratocyst is a common cystic lesion of the jaw,which arises from the remnants of dental lamina.
- It is named as keratocyst because the cyst epithelium produces so much keratin that it fils the cyst lumen.
- Odontogenic cysts have more aggressive course than any other cystic lesion of jaw and for this reason these are sometimes known as benign cystic neoplasms.
Recent concept of Odontogenic Keratocyst
- Keratocystic odontogenic tumor is now listed as ‘odontogenic keratocyst (OKC)’ in the 2017 classification of developmental odontogenic cysts.
- WHO 2005 classification reclassifid this unique lesion as a neoplasm and renamed it as ‘keratocystic odontogenic tumor’ because of the high recurrence rate, aggressive clinical behavior, association with nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome, and mutations in the PTCH tumor suppressor gene.
The WHO 2017 classifiation reverted back to the original and well accepted terminology of ‘odontogenic keratocyst’ because many papers showed that the PTCH gene mutation could be found in nonneoplastic lesions, including dentigerous cysts.
It has also been reported that marsupialisation is an effctive treatment for the odontogenic keratocyst and may be associated with reversion of the epithelium to normal, and with lower recurrence rates,these features are not normally associated with neoplasia.
So after considering all the available data, the WHO consensus group concluded that further research is needed,but at the present time, there was insuffient evidence to support a neoplastic origin of the odontogenic keratocyst.
It was decided therefore that odontogenic keratocyst remains the most appropriate name for this lesion, and keratocystic odontogenic tumor was removed from the WHO 2017 classifiation of odontogenic cysts.
Pathogenesis of Odontogenic Keratocyst
Odontogenic keratocyst mainly arises from the:
- Dental lamina or its remnants.
- Primordium of developing tooth germ or enamel organ.
- Sometimes from basal cell layer of oral epithelium.
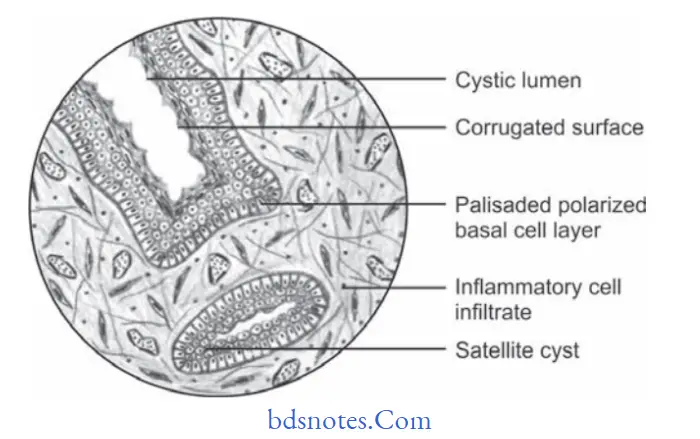
Histopathological Features of Odontogenic Keratocyst
- A parakeratin surface which is usually corrugated rippled or wrinkled.
- Uniformity of thickness of epithelium is generally between 6 to 10 cells in depth.
- Prominent palisaded, polarized basal cell layer often described as having a “picket fence” or “tombstone”appearance.
- Occasionally orthokeratin is found but if present, parakeratin is evident.
- Connective tissue shows “Daughter cells” or “Satellite cysts”.
- Lumen of keratocyst may be filed with thin straw-colored flid or with thick creamy material.
- Sometimes a lumen contains a great deal of keratin while at other times it has litte cholesterol as well as hyaline bodies at the site of inflmmation.
Clinical Features of Odontogenic Keratocyst
- Peak incidence is between 2nd and 3rd decades of life.
- It is found more frequently in males as compared to females.
- Mandible is affcted more commonly than maxilla.
- In mandible, the majority of cysts occurs in ramus third molar area, followed by fist and second molar area and then the anterior mandible.
- It is asymptomatic unless they become secondarily infected in which case patient complains of pain, soft tissue swelling and drainage.
- Occasionally, they experience paresthesia of lower lip and teeth.
- There is often one tooth missing from the dental arch.
- Expansion and thinning of bone may result in pathological fracture.
- Maxillary odontogenic keratocyst tends to be secondarily infected with greater frequency than the mandibular ones,due to its vicinity to maxillary sinus.
Radiological Features of Odontogenic Keratocyst
- Odontogenic keratocyst is oval in shape and it extends to the body of mandible with mediolateral expansion.
- It is very small in size or it can exceed the diameter of 5 cm.
- Margins of the cyst are hyperostotic.
- Mostly odontogenic keratocyst is unilocular and have smooth borders while some of the cysts show irregular borders too.
- Radiolucency is seen in the cystic part which appears to be hazy if keratin is present in the cavity.
- Radiolucency is surrounded by thin sclerotic rim.
- In some of the cases perforation of lingual and buccal cortical plates is seen.
- Displacement of inferior alveolar canal is seen downwards.
Question.4.Classify cysts of oral region. Discuss radicular cyst in detail.
Or
Write note on radicular cyst.
Or
Write short note on radicular cyst.
Or
Classify odontogenic cyst. Describe the pathogenesis, clinical, radiological, and histopathological features of radicular cyst.
Answer.
Radicular Cyst
- It is also called as apical periodontal cyst or periapical cyst or dental root end cyst.
- It is an inflammatory odontogenic epithelial cyst.
- It is a common sequelae in progressive changes associated with bacterial invasion and death of the dental pulp.
- It most commonly occurs at the apices of the teeth.
Pathogenesis Of Radicular Cyst
Radicular cyst develops due to the proliferation and subsequent cystic degeneration of the “epithelial cell rests of Malassez”, in the periapical region of a nonvital tooth.
The process of development of this cyst occurs in various stages:
- Phase of initiation
- Phase of proliferation
- Phase of cystifiation
- Phase of enlargement
- Phase of initiation: During this phase, the bacterial infection of the dental pulp or direct inflmmatory effct of necrotic pulpal tissue, in a nonvital tooth causes stimulation of the “cell rest of Malassez” which are present within the bone near the root apex of teeth.
- Phase of proliferation: The stimulation to the cell rests of Malassez leads to excessive proliferation of these cells,which leads to the formation of a large mass or island of immature proliferating epithelial cells at the periapical region of the affcted tooth.
- Phase of cystifiation: Once a large bulk of the cell rest of Malassez is produced, its peripheral cells get adequate nutritional supply but its centrally located cells are often deprived of proper nutritional supply. As a result the central group of cells undergo ischemic liquefactive necrosis while the peripheral group of cells survive. This eventually gives rise to the formation of a cavity that contains a hollow space or lumen inside the mass of the proliferating cell rest of Malassez and a peripheral lining of epithelial cells around it.
- Phase of enlargement: Once a small cyst is formed, it enlarges gradually by the following mechanisms:
- Higher osmotic tension of the cystic fluid causes progressive increase in the amount of flid inside its lumen and this causes increased internal hydrostatic tension within the cyst. The process results in cyst expansion due to resorption of the surrounding bone.
- The epithelial cells of the cystic lining release some bone resorbing factors like prostaglandins and collagenase, etc. which destroy the bone and facilitate expansion of the cyst.
Clinical Features
- It most commonly occurs on 3rd, 4th and 5th decades of the life.
- It is more common among the males.
- Maxillary anteriors are most commonly affcted.
- Majority of cases are asymptomatic.
- It is associated with the nonvital tooth.
- Small cystic lesions are asymptomatic.
- Large lesions often produce a slow enlarging bony hard swelling of the jaw with expansion of cortical plates.
- Severe bone destruction produces “springiness” of jaw bone.
- If the cyst is secondarily infected it leads to the formation of the abscess, which is called “cyst abscess”.
Histological Features
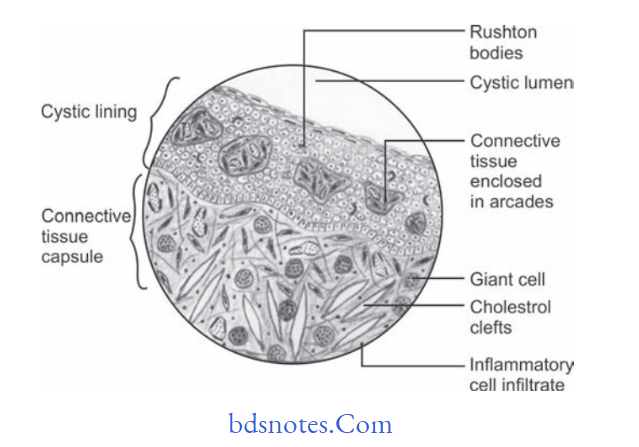
- Radicular cyst is lined by the stratifid squamous epithelium.
- It is lined by pseudostratifid, columnar or respiratory
type Of Epithelium. - Hyaline bodies or Rushton bodies often found in the great numbers in the epithelium of apical periodontal cyst.
- Collagenous connective tissue makes the wall of radicular cyst.
- Abundant firoblast can be identifid within the cystic wall.
- Cystic wall presents inflmmatory infitrate which contains lymphocytes, plasma cells.
- Other histological fidings within the cyst wall are erythrocytes, area of hemorrhage, occasional spicules of dystrophic bone, multinucleated giant cells and cholesterol crystals.
Radiological Features
It is round or oval radiolucency of variable size which is generally well delineated and is most likely with marked radiopaque rim.
Treatment
Root canal treatment
Extraction of involved tooth
Enucleation or marsupialization of large lesion is done.
Question.5. Write note on dermoid cyst.
Answer. It is also known as dermoid cystic tumor or cystic teratoma.
- It is a developmental cyst derived from the remnants of the embryonic skin.
- It is hamartomatous tumor containing multiple sebaceous glands and almost all skin adnexa, this may consist of substances such as nails and dental cartilage like and bone like structures.
Clinical Features Of Dermoid Cyst
- It occurs in young children.
- Dermoid cyst occurs most commonly on face, neck or scalp.
- In addition to skin dermoid cyst can be intracranial, intraspinal or perispinal.
- It is a painless swelling having the dough consistency.
- A cyst which develops above the mylohyoid muscle and presents the sublingual swelling in the midline.
- Cyst below the mylohyoid muscle presents submental and submandibular swelling in the midline.
Histological Features Of Dermoid Cyst
- Dermoid cysts in the skin are lined by the orthokeratinized stratifid squamous epithelium which exhibit hair follicles,sebaceous glands and erector pili muscles.
- Cavity lumen is often filed with the sebum, keratin and hair shafts.
- Cyst capsule is composed of narrow zone of compressed connective tissue.
Treatment Of Dermoid Cyst
Surgical excision is done.
Question.6. Write note on epidermoid cyst.
Answer. It is also called epidermoid inclusion cyst or epidermoid cyst or keratin cyst or sebaceous cyst.
- Epidermoid inclusion cysts are the result of implantation of epidermoid elements and its subsequent cystic transformation.
Clinical Features Of Epidermoid Cyst
- It is most common in 3rd and 4th decades of life.
- It is twice as common in men as in women.
- Common sites are face, trunk, neck extremities and scalp.
- Epidermoid cyst appears as fim, round, mobile, flsh colored to yellow or white subcutaneous nodules of variable size. In some patients, it contains melanin pigments.
- Discharge of foul smelling cheese like material is a common complaint.
- Sometimes cyst becomes inflmed and infected resulting in pain and tenderness.
- When located orally, it can cause diffilty in feeding,swallowing and even speaking.
Histological Features Of Epidermoid Cyst
- Cyst is lined by the stratifid squamous epithelium with glandular diffrentiation.
- Cyst is filed with desquamated keratin disposed in a lamellar pattrn.
- Dystrophic calcifiation and reactive foreign body reaction are seen associated with the cystic capsule.
- Pigmented epidermoid cyst may demonstrate melanin pigment in the wall and a keratin may present.
- A surrounding infitrate of melanocytes and macrophages may be observed.
Treatment Of Epidermoid Cyst
Surgical excision is done.
Question.7. Write note on globulomaxillary cyst.
Answer. As per the older concept globulomaxillary cyst was a fisural cyst that arose from epithelium entrapped during fusion of the globular portion of the medial nasal process with the maxillary process.
- As per the recent concept globular portion of the medial nasal process is primarily united with the maxillary process and fusion does not occur.
Therefore, epithelial entrapment should not occur during embryologic development of this area. - All cysts in the globulomaxillary region, i.e. between the lateral incisor and canine teeth can be explained on an odontogenic basis.
- Many are lined by inflmed stratifid squamous epithelium and are consistent with periapical cysts
- It was also theorized that some of these lesions may arise from inflmmation of the reduced enamel epithelium at the time of eruption of the teeth.
- In some cases cysts in the globulomaxillary area may be lined by pseudostratifid, ciliated, columnar epithelium. Such cases provide credence to the fisural theory of origin.
- Since fisural cyst in this region probably does not exist, the term globulomaxillary cyst should no longer be used.
- When a radiolucency between the maxillary lateral incisor and canine is encountered, the clinician should fist consider an odontogenic origin for the lesion.
Question.8. Write notes on benign cervical lymphoepithelial cyst.
Answer. Benign cervical lymphoepithelial cyst is also known as branchial cleft cyst.
Pathogenesis Of Branchial Cleft Cyst
It originates from cystic transformation of gland epithelium entrapped in the oral lymphoid aggregates during embryogenesis.
Clinical Features Of Branchial Cleft Cyst
- It is located superfiially in the neck, close to the angle of mandible, anterior to sternocleidomastoid muscle.
- It occurs at all the ages with a fairly equal distribution from 1st to 6th decades.
- Neck lesions vary in size from small to very large.
- There is swelling, which may be progressive or intermittnt and pain may also be a feature.
- Lymphoepithelial cyst generally present as an asymptomatic, circumscribed, movable swelling on lateral aspect of the neck.
- It may be unilateral or bilateral.
Histopathology Of Branchial Cleft Cyst
- Cystic cavity is lined by thin stratifid squamous epithelium.
- Cyst is generally embedded in a circumscribed mass of lymphoid tissue.
- Capsule of the cyst also present variable amount of connective tissue, being infitrated by lymphocytes, plasma cells, macrophages and some multinucleated giant cells.
- Cystic lumen is filed up with either a thin watery flid or a thick gelatinous material.
Treatment Of Branchial Cleft Cyst
It is removed by local surgical incision.
Question.9.Classify odontogenic cyst. Write in detail on radicular cyst.
Answer.
Classification of Odontogenic Cyst
WHO (2017) Classification of Odontogenic Cysts
- Odontogenic cysts of inflammatory origin
- Radicular cyst
- Inflammatory collateral cysts
- Odontogenic developmental cysts
- Dentigerous cyst
- Odontogenic keratocyst
- Lateral periodontal cyst and botryoid odontogenic cyst
- Gingival cysts
- Glandular odontogenic cyst
- Calcifying odontogenic cyst
- Orthokeratinized odontogenic cyst
Question.10. Enumerate nonodontogenic cysts of oral cavity. Write about histopathology of odontogenic keratocyst.
Answer. Enumeration of nonodontogenic cysts of oral cavity
According to shear
- Nasopalatine duct cyst
- Median palatine, median alveolar and median mandibular cyst
- Globulomaxillary cyst
- Nasolabial cyst.
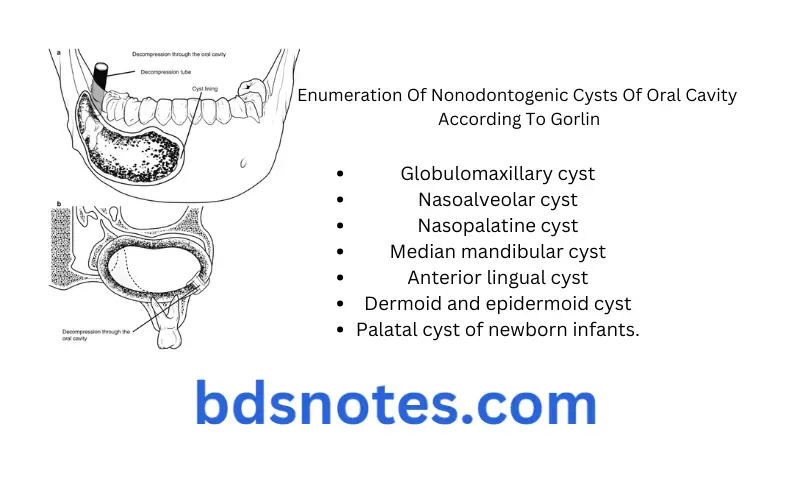
According to gorlin
- Globulomaxillary cyst
- Nasoalveolar cyst
- Nasopalatine cyst
- Median mandibular cyst
- Anterior lingual cyst
- Dermoid and epidermoid cyst
- Palatal cyst of newborn infants.
According to WHO 2007
- Nasopalatine duct cyst.
Question.11. Write note on eruption cyst.
Answer. It is defied as odontogenic cyst with histologic features of a dentigerous cyst and that surrounds a tooth crown which has erupted through bone but not soft tissue and is clinically visible as a soft flctuant mass on alveolar ridges.
Clinical Features Of Eruption Cyst
- Most commonly found in children.
- It arises most frequently anteriorly to fist permanent molar.
- Lesion appears as circumscribed, flctuant, often translucent swelling of alveolar ridge at site of erupting tooth.
- When the cystic cavity contains blood, swelling appears deep blue or purple so it is known as eruption hematoma.
- Swelling is painless since it is infected.
Histological Features Of Eruption Cyst
- On microscopic examination stratified squamous
epithelium of overlying gingiva is seen. - Epithelium is separated from cyst by a strip of dense connective tissue.
- There is presence of mild chronic inflammatory cell infitrate.
- In non-inflmed areas epithelial lining of cyst is of reduced enamel epithelium.
Treatment Of Eruption Cyst
No treatment is necessary as cyst often ruptures spontaneously.
Question.12. Describe in brief reasons for recurrence of odontogenic keratocyst.
Answer. Following are the reasons for recurrence of odontogenic keratocyst:
- Odontogenic keratocyst multiply in some patients including the occurrence of satellite cysts which may be retained during an enucleation procedure.
If enucleation procedures are incomplete may be new cyst arise from retained satellite microcysts or retained mural cell islands. - Linings of odontogenic keratocyst are thin and fragile and are diffilt to enucleate. Portions of lining may remain left behind and lead to recurrence.
- When OKC is enucleated in a single piece chances of recurrence are low while when it is removed in multiple pieces chances of recurrence is high.
This is because in multiple pieces at times remnants of cyst remain which lead to recurrence. - OKCs may also arise from proliferation of basal cells of oral mucosa also known as basal cell hamartias in third molar region and ascending ramus of mandible.
It was observed that there is perforation of overlying bone and firm adhesion of cyst to overlying mucosa.
So when cysts were surgically removed overlying mucosa should be excised with them to prevent recurrence from residual basal cell proliferations. If overlying mucosa is not excised or it remains it leads to recurrence.
Question.13.Write short note on histopathology of COC.
Answer. It is also known as calcifying odontogenic cyst or Calcifying epithelial odontogenic cyst.
Histopathology Of COC
- Epithelial lining of COC shows prominent basal cell layer consisting of palisaded columnar or cuboidal cells and hyperchromatic nuclei which are polarized away from basement membrane.
- Epithelium is 6–8 cell layer thick.
- Budding from the basal cell layer into adjacent connective tissue and epithelial proliferations into lumen are seen.
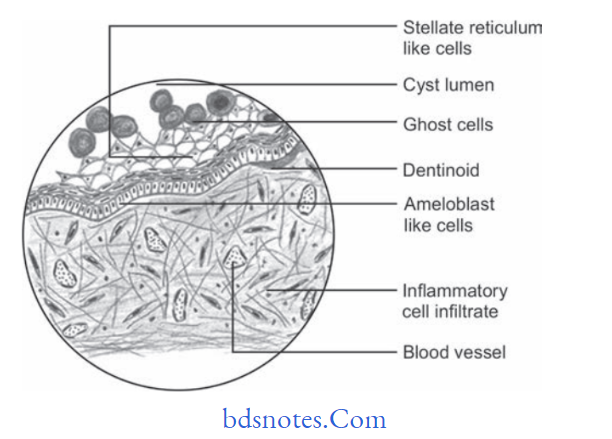
- Ghost cells: They are enlarged, ballooned shape, ovoid or elongated elliptoid epithelial cells.
They are eosinophilic.
They are found in thick areas of epithelial lining.
Cell outlines of these cells are well defined and at times they may be blurred. They are seen singly and also present in groups.
Few ghost cells also show nuclear remnants.
Ghost cells have abnormal type of keratinization and have affinity to calcify. - Ghost cells also may remain in contact to connective tissue wall of cyst where they lead to foreign body reactions with formation of multinucleated giant cells.
- An atubular dentinoid is also seen in the wall close to epithelial lining and also in relation to epithelial proliferations.
- Dentinoid found particularly in contact with masses of ghost cells.
Question.14.Classify cysts of oral region. Give a detailed account of clinical, radiological, and histopathological features of odontogenic keratocyst.
Or
Classify cyst of jaw. Write in detail clinical radiological and histopathological features of odontogenic keratocyst.
Answer.
Radiological Features
- Odontogenic keratocyst is oval in shape and it extends to the body of mandible with mediolateral expansion.
- It is very small in size or it can exceed the diameter of 5cm.
- Margins of the cyst are hyperostotic.
- Mostly odontogenic keratocyst is unilocular and have smooth borders while some of the cysts show irregular borders too.
- Radiolucency is seen in the cystic part which appears to be hazy if keratin is present in the cavity.
- Radiolucency is surrounded by thin sclerotic rim.
- In some of the cases perforation of lingual and buccal cortical plates is seen.
- Displacement of inferior alveolar canal is seen downwards.
Question.15.Give classification of osteomyelitis. Discuss in detail clinical features, etiology, histopathology of odontogenic keratocyst.
Answer.Classification of osteomyelitis
- Acute osteomyelitis
- Acute suppurative osteomyelitis
- Acute subperiosteal osteomyelitis
- Acute periostitis
- Chronic osteomyelitis:
- Non-specific type:
- Chronic intramedullary osteomyelitis
- Chronic focal sclerosing osteomyelitis
- Chronic diffuse sclerosing osteomyelitis
- Chronic osteomyelitis with proliferative periostitis
- Chronic subperiosteal osteomyelitis
- Chronic periostitis
- Specific type:
- Tuberculous osteomyelitis
- Syphilitic osteomyelitis
- Actinomycotic osteomyelitis
- Non-specific type:
- Radiation-induced osteomyelitis
- Idiopathic osteomyelitis.
Etiology of odontogenic Keratocyst
The cyst arises from:
- Dental lamina or its remnants.
- Primordium of developing tooth germ or enamel organ
- Basal cell layer of oral epithelium.
Question.16. Write short note on rushton bodies.
Answer. Rushton bodies are seen in the histological picture of radicular cyst or residual cyst.
- Rushton body is a hyaline body is found in great numbers in epithelium of radicular cyst or residual cyst.
- Rushton bodies are linear, straight or curved or of hair pain shaped.
- Rushton bodies measure upto 0.1 mm
- Rushton bodies appear amorphous in structure,eosinophilic in reaction and are britte in nature.
- They are sometimes concentrically laminated and frequently fractured.
Rushton Bodies Origin
Related to origin of rushton bodies two views were put forward i.e.
- Rushton bodies were of odontogenic epithelial origin and are probably a form of keratin. — By Shear
- Hyaline bodies has hematogenous origin and they were derived from thrombi in venules of connective tissue that had become varicose and strangled by the cuffs of epithelium which encircle it and these bodies reacted histochemically as hemoglobin.
According to the authors who had given this view also suggested that thrombi shrink centrifugally and undergo splitting or calcify.

Leave a Reply