Question 1. Write about origin, innervations, action of muscles of eyeball (or) Extraocular muscles. (or) Oblique muscle of eyeball (or) Action of oblique muscle of eyeball
Answer:
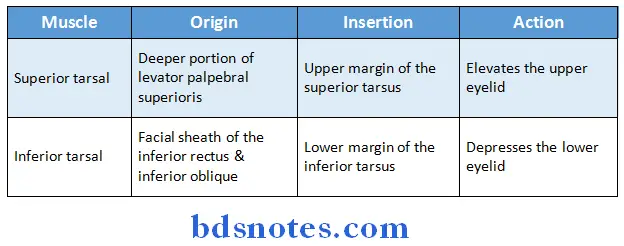
Muscles of Eyeball:
1. Involuntary muscles:
Read And Learn More: BDS Previous Examination Question And Answers
2. Voluntary muscles:
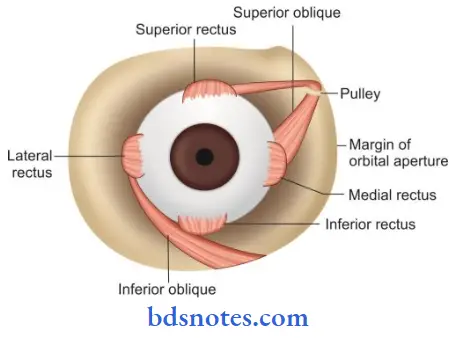
Muscles of Eyeball Applied anatomy:
- Paralysis of muscles of eyeball causes various symptoms
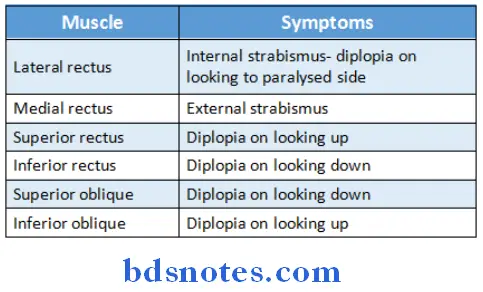
Question 2. Nerves of the orbit (or) Lateral rectus muscle of eyeball
Answer:
1. Lateral Rectus Muscle Of Eyeball Optic nerve:
- Lateral Rectus Muscle Of Eyeball Optic nerve is the nerve of sight
- Lateral Rectus Muscle Of Eyeball Optic nerve is made up of the axons of cells in the ganglionic layer of the retina
- Lateral Rectus Muscle Of Eyeball Optic nerve emerges from the eyeball 3 or 4 mm nasal to its posterior pole
- Lateral Rectus Muscle Of Eyeball Optic nerve is enclosed in three meningeal sheaths
- Lateral Rectus Muscle Of Eyeball Optic nerve cannot degenerate once it is cut
2. Lateral Rectus Muscle Of Eyeball Oculomotor nerve:
- Lateral Rectus Muscle Of Eyeball Oculomotor nerve is third cranial nerve
- Lateral Rectus Muscle Of Eyeball Oculomotor nerve is distributed to the extraocular & intraocular muscles
- Functional components:
- General somatic efferent
- General visceral efferent
- General somatic afferent
Optic nerve Nucleus:
- Optic nerve Nucleus is situated in the ventromedial part of central grey matter of midbrain at the level of superior colliculus
3. Trochlear nerve:
- Trochlear nerve is fourth cranial nerve
- Trochlear nerve supplies superior oblique muscle of the eyeball
- Functional components:
- General somatic efferent
- General somatic afferent
Nucleus:
- Nucleus is situated in the ventromedial part of central grey matter of midbrain at the level of inferior colliculus
4. Abducent nerve:
- Abducent nerve is sixth cranial nerve
- Abducent nerve supplies the lateral rectus muscle of the eyeball
- Abducent nerve Functional components:
- General somatic efferent
- General somatic afferent
Abducent nerve Nucleus:
Abducent nerve Nucleus is situated in the upper part of the floor of fourth ventricle in the lower pons
5. Branches of ophthalmic & maxillary divisions of the trigeminal nerve:
- Branches of ophthalmic divisions:
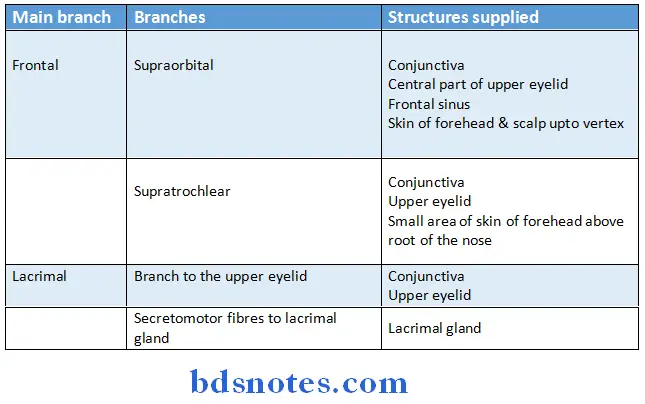
- Branches of maxillary division:
- Infraorbital nerve:
- Infraorbital nerve enters the orbit through the inferior orbital fissure
Branches:- Middle superior alveolar nerve
- Anterior superior alveolar nerve
- Terminal branchespalpebral, nasal & labial
- Infraorbital nerve enters the orbit through the inferior orbital fissure
- Zygomatic nerve:
- Zygomatic nerve enters the orbit through the lateral end of the inferior orbital fissure
Branches:
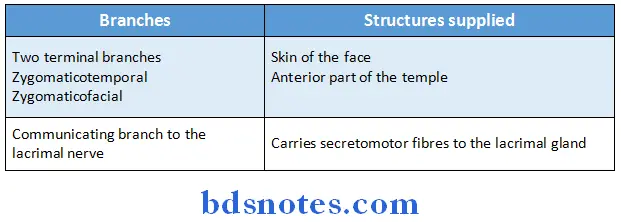
6. Sympathetic nerves:
- Arises from the internal carotid plexus
- Sympathetic nerves enter the orbit through
- Ophthalmic nerve
- Nasociliary nerve
- Long Ciliary branches
- Plexus surrounding ophthalmic artery
- Direct branch from internal carotid plexus
- Oculomotor, Trochlear, Abducent & ophthalmic nerves
Question 3. Give the positions, connections & branches of ciliary ganglion (or) Ciliary Ganglion
Answer:
Ciliary Ganglion Position:
- Ciliary ganglion lies near the apex of the orbit between the optic nerve & the tendons of the lateral rectus muscle
- Ciliary Ganglion Position is related to nasociliary nerve
Ciliary Ganglion Roots:
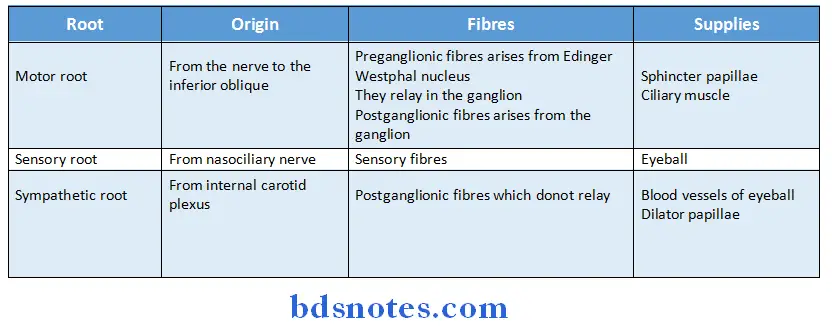
Ciliary Ganglion Branches:
- The ganglion gives off 810 short Ciliary nerves which further divide into 1520 branches
- Ciliary Ganglion Branches also contains fibres from the roots of te ganglion
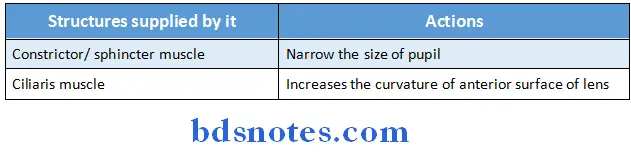
Ciliary Ganglion Actions of its branches:
- Narrowing the size of pupil by supplying constrictor muscle
- Increasing the curvature of anterior surface of lens by supplying ciliaris muscle
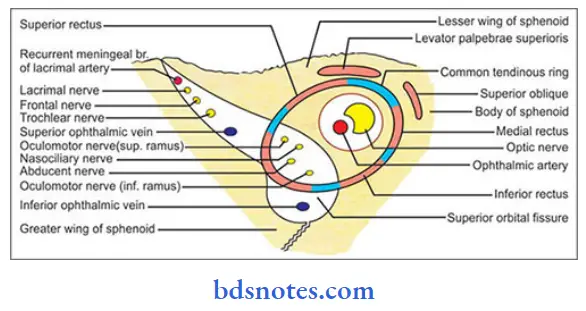
Question 4. Vessels of the orbit
Answer:
1. Ophthalmic artery:
- Ophthalmic artery is a branch of the cerebral part of the internal carotid artery
- Ophthalmic artery enters the orbit through the optic canal
Vessels of the orbit Branches:
- Central artery of retina
- Branches arising from the lacrimal artery
- Branches given to the lacrimal gland
- 2 zygomatic branches
- Lateral palpebral branches supplying the eyelids
- A recurrent meningeal branch
- Muscular branches supplying muscles of orbit
- Branches arising from the main trunk
- Posterior ciliary arteries
- Supraorbital & Supratrochlear
- Anterior & posterior ethmoidal
- Medial palpebral
- Dorsal nasal
2. Ophthalmic veins:
- Superior ophthalmic vein
- Lies above the optic nerve
- Receives tributaries from branches of ophthalmic artery
- Drains into cavernous sinus
- Inferior ophthalmic vein
- Lies below the optic nerve
- Receives tributaries from the lacrimal sac, lower orbital muscles & eyelids
- Joins superior ophthalmic vein
- Drains into cavernous sinus
3. Lymphatics:
- Drains into preauricular parotid lymph node
Question 5. Ophthalmic artery
Answer:
Ophthalmic artery Origin:
- Ophthalmic artery Origin is a branch of the cerebral part of the internal carotid artery
Ophthalmic artery Course:
- Ophthalmic Artery Course enters the orbit through the optic canal
- Pierces the dura mater
- Runs along the medial wall of orbit
- Terminates near the medial angle of the eye by dividing into the supratrochlear and dorsal nasal branches
Ophthalmic artery Branches:
1. Central artery of retina
- First and most important branch of ophthalmic artery
2. Branches arising from the lacrimal artery
- Branches given to lacrimal gland
- Two zygomatic branches
- Lateral palpebral branches supplying the eyelids
- A recurrent meningeal branch
- Muscular branches supplying muscles of orbit
3. Branches arising from the main trunk
- Posterior ciliary arteries
- Supraorbital and supratrochlear
- Anterior and posterior ethmoidal
- Medial palpebral
- Dorsal nasal
Ophthalmic artery Applied aspect:
- Central artery of retina is only arterial supply to retina
- If it gets blocked then it leads to sudden blindness
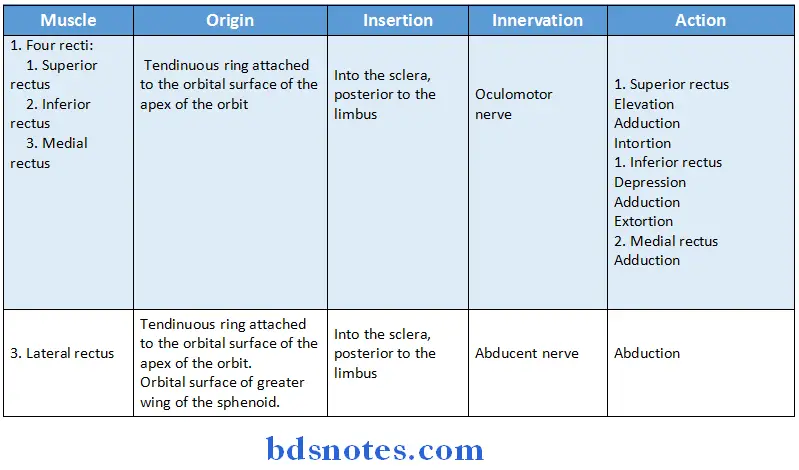
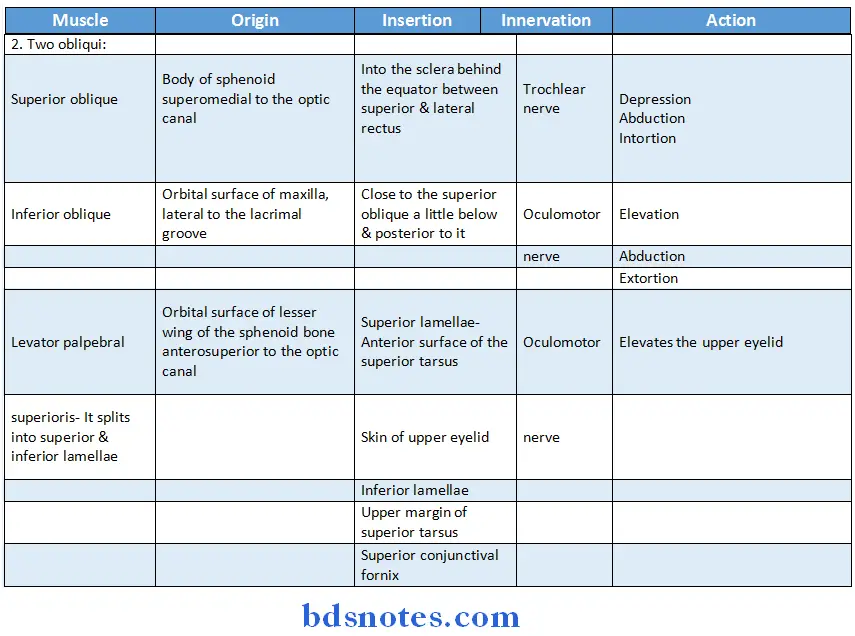
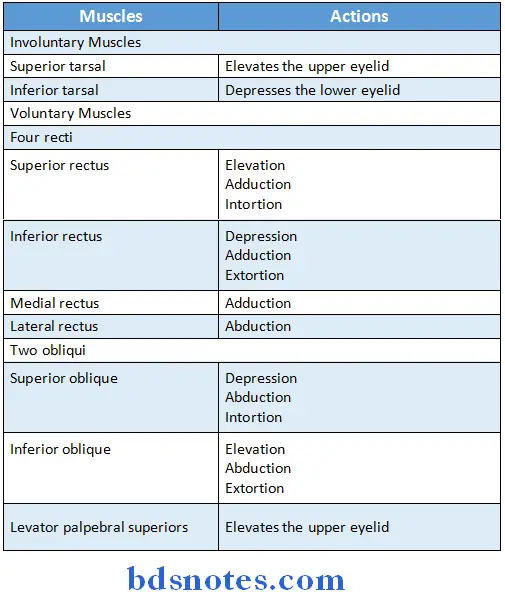
Question 6. Extraocular muscles and their actions.
Answer:
Question 7. Nasociliary nerve. (or) Name branches of nasociliary nerve
Answer:
- Nasociliary is one of the terminal branches of the ophthalmic division of the trigeminal nerve
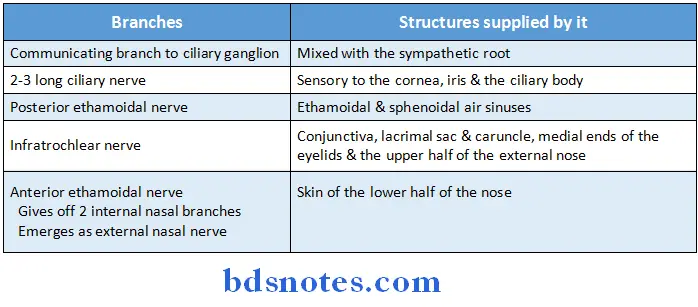
Question 8. Short ciliary nerve
Answer:
- The Postganglionic parasympathetic fibres from ciliary ganglion are distributed to the eyeball through the short ciliary nerves
Question 9. Fascial sheath of eyeball
Answer:
- Fascial sheath of eyeball is a layer of fascia that encloses a major part of eyeball
- Fascial sheath of eyeball is pierced by
-
- Tendons of various extraocular muscle
- Ciliary vessels & nerve
- It gives off a number of expansions like
- Tubular sheath
- Medial check ligament
- Lateral check ligament
- It gives off a number of expansions like
Fascial sheath of eyeball Extend:
- From the optic nerve to the sclerocorneal junction
Fascial sheath of eyeball Attachments:
- Posteriorly to sclera around the point of entrance of optic nerve
- Anteriorly to the sclera near the edge of cornea
Fascial sheath of eyeball Significance:
- The eyeball can freely move within this sheath
Question 10. Extraocular muscles and their nerve supply
Answer:
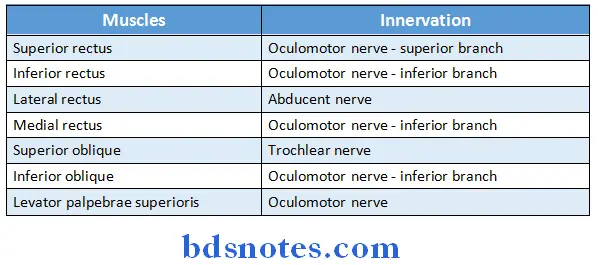
Question 11. Nerve supply and actions of superior oblique
Answer:
Superior Oblique Muscle of Eyeball:
- Superior Oblique Muscle of Eyeball is voluntary muscle of eyeball
superior oblique Nerve Supply:
- superior oblique Nerve Supply is supplied by trochlear nerve
superior oblique Actions:
- Depresses eyeball
- Abduction of eyeball
- Intortion of eyeball
Question 12. Infraorbital nerve
Answer:
- Infraorbital nerve is branch of ophthalmic division of trigeminal nerve
- Infraorbital nerve enters the orbit through the inferior orbital fissure
Infraorbital nerve Branches:
- Middle superior alveolar nerve
- Anterior superior alveolar nerve
- Terminal branches palpebral, nasal and labial
Question 13. Superior rectus muscle of eyeball and it’s action
Answer:
- Superior rectus muscle of eyeball is an extraocular muscle of orbit
- Superior rectus muscle of eyeball has origin in the back of the orbit in a fibrous ring called the annulus of Zinn.
- This ring is attached to the orbital surface of the apex of the orbit.
- The fibres are inserted into the sclera posterior to the limbus
- Superior rectus muscle of eyeball is supplied by the superior branch of oculomotor nerve.
Superior rectus muscle of eyeball Actions:
- Elevation
- Adduction
- Intortion
Superior rectus muscle of eyeball Applied anatomy:
- Superior rectus muscle of eyeball is the only muscle that is capable of elevating the pupil when it is in a fully abducted position.
Question 14. Optic canal
Answer:
- Optic canal leads to the orbit
- Optic canal is bounded
- Laterally by lesser wing of sphenoid
- Front and behind by the two roots of the lesser wing
- Medially by the body of sphenoparietal
- Structures passing through it are:
- Optic nerve
- Ophthalmic artery.
Question 15. Functional components of oculomotor nerve.
Answer:
Functional components of oculomotor nerve are:
- General somatic efferent
- General visceral efferent
- General somatic afferent

Leave a Reply