Cestodes —Tapeworms
Question 1. Write a note on the life cycle of Echinococcus granulosus.
Answer:
- Echinococcus granulosus is also known as dog tapeworm.
- It is a cestode, and it is the causative agent of hydatid
disease.
Life Cycle of Echinococcus granulosus
- Definitive host: Dog (also fox, wolf, and jackal)
- Intermediate host: Sheep, cattle, pig, goat, horse, and human being

Question 2. Write briefly about the hydatid cyst.
Or
Write short note on hydatid cyst. (Dec 2017, 3 Marks)
Answer:
Hydatid Cyst
- A Hydatid cyst is the larval form that develops in the tissue of the intermediate host.
- Hydatid cyst is found in the various organs of humans as well as intermediate hosts.
- It represents the scolex of future adult worms and remains invaginated inside the vesicular body.
- In humans, a hydatid cyst is unilocular, subspherical in shape, and fully filled with fluid.
- The growth rate of hydatid cysts is 1 to 5 cm/year.
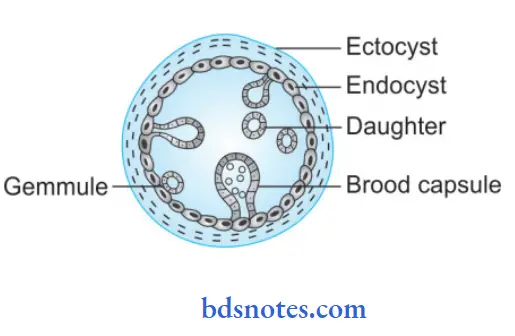
- The cyst wall secreted by the embryo consists of two layers, i.e.
- Outer cuticular layer Or ectocyst: It is the laminated hyaline membrane that appears as a white part of a boiled egg. Its thickness is 1 mm and is elastic
- Inner germinal layer or encyst: This is cellular, nucleate, and thin. It is 22 to 25 µ. This layer is the vital layer that gives rise to brood capsules with scolices, specific hydatid fluid, and an outer layer.
- In some of the hydatid cysts, brood capsules do not develop or if they develop they lag scolices these cysts are known as acephalocysts.
- Hydatid fluid:
- It is a clear, colorless, pale yellow fluid.
- It has a low specific gravity
- It is slightly acidic, i.e. pH 6.7
- It consists of sodium chloride, sodium sulfate, sodium phosphate, and sodium as well as calcium salts of succinic acid.
- As its nature is antigenic, it is used for Casoni’s test.
- This is highly toxic and when absorbed can lead to anaphylaxis
- Hydatid fluid consists of granular deposits that settle at the bottom, known as hydatid sand. It consists of brood capsules, free scolices, and loose hooklets.

Leave a Reply