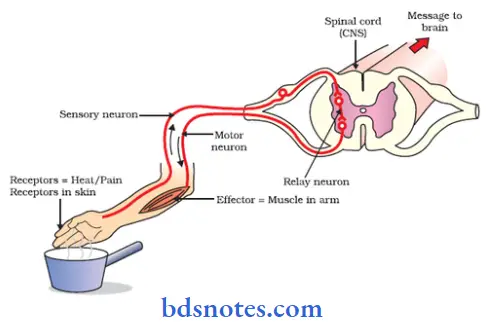
Question 1. Draw a diagram to show different parts of reflex arc. Describe properties of reflex.
Answer:
Reflex arc:
- The anatomical nervous pathway for a reflex action is called reflex arc.
Parts:
1. Receptor:
- It is the end organ that receives the stimulus.
Read And Learn More: BDS Previous Examination Question And Answers
2. Afferent nerve:
- It transmits sensory impulses from receptor to the center.
3. Center:
- Receives sensory impulses via afferent nerve fibers.
- It generates appropriate motor impulse
- It is located in the brain or spinal cord.
4. Efferent nerve:
- Transmits motor impulses from center to the effector organ.
5. Efferent organ:
- It shows response to the stimulus.
Properties of reflex:
1. One way conduction [Bell – Megendie Law]:
- Impulses are transmitted in only one direction via reflex arc.
- They are transmitted from receptors to center then to effector organ.
2. Reaction Time:
- It is the time interval between application of stimulus and the onset of reflex.
- It depends upon length of the nerve fibers.
3. Summation:
- Repeated or simultaneous stimulation of motor neurons with sub minimal stimuli exhibit the phenomenon of summation.
Types:
Spatial summation:
- In this the stimuli is simultaneously applied to different presynaptic neurons.
Temporal summation:
- Here a single nerve fiber is stimulated repeatedly with sub-threshold stimuli which are summed up to give response.
4. Occlusion:
- When muscle with two nerve fibers are stimulated simultaneously, the tension developed is less than the sum of the tension developed when each nerve is stimulated separately.
- This phenomenon is called occlusion.
- It occurs due to overlapping of the nerve fibers during the distribution.
5. Subliminal fringe:
- When some muscle with two nerve fibers are stimulated simultaneously, the tension developed is greater than the sum of the tension developed when each nerve is stimulated separately.
- This phenomenon is called subliminal fringe.
- It is due to spatial summation.
6. Recruitment:
- When an excitatory nerve is stimulated with a stimulus of constant strength for a long time, there is a progressive increase in the response of reflex.
- This phenomenon is called recruitment.
7. After discharge:
- Even after the cessation of the stimulus the reflex response continues for some more time.
8. Rebound phenomenon:
- A reflex response that is diminished by stimulation of an afferent nerve will attain full power when the stimulation ceases is known as rebound phenomenon.
9. Fatigue:
- The reflex response obtained gradually gets lessened.
- It is said to be in fatigue.
10. Habituation:
- If the stimulus is benign and repeated at frequent intervals, the response declines and disappears, it is called habituation.
11. Sensitization:
- It is opposite to habituation.
12. Reciprocal innervations:
- Stimulation of an afferent fibers results in contraction of the agonist and relaxation of the antagonists.
- This called reciprocal innervation.
Question 2. Add a note on hemisection of spinal cord. (or) Brown-squard syndrome.
Answer:
Brown-squard syndrome Definition:
- A lesion involving one lateral half of the spinal cord is termed as hemisection.
Brown-squard syndrome Synonym:
- Brown – sequard syndrome.
Brown-squard syndrome Cause:
- Injury during accidents.
Brown-squard syndrome Effets:
- The effects are seen below the level of lesion and at the level of lesion.
- These differ on the same side and one the opposite side of the lesion.
1. Effects seen below the level of lesion:

2. Effects seen at the level of lesion:

Question 3. Name of the ascending tracts of spinal cord. Describe origin, course, termination and functions of any one. (or) Spinothalamic tract.
Answer:
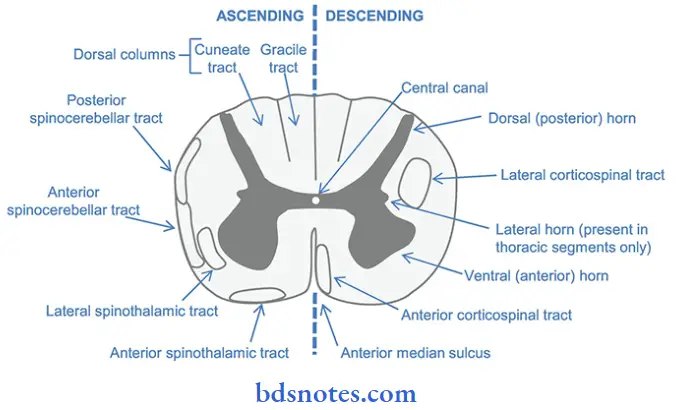
Ascending tracts of spinal cord:
- They carry a group of sensory fibers from the receptor to the CNS.
- They are.
1. Tracts in dorsal white column:
- Fasciculus gracilis
- Fasciculus cuneatus.
2. Tracts in lateral white column:
- Lateral spinothalamic tract.
- Dorsal spinocerebellar tract.
- Ventral spinocerebellar tract.
- Spinotectal tract.
- Spinoreticular tract.
- Spino-olivary tract.
- Spino-vestibular tract.
3. Tract in anterior white funiculus:
- Anterior spinothalamic tract.
Spinothalamic tract:
- There are two such tracts.
- Anterior spinothalamic tract.
- Lateral spinothalamic tract.
spinal cord Origin:

Course:
spinal cord Both tracts:

spinal cord Termination:
- The fibers from both the tracts terminate in the central posterolateral nucleus of thalamus.
- Cells of this nucleus forms the third order neurons.
- Fibers from this nucleus carry the impulses to sensory cortex of cerebral cortex.
spinal cord Function:
1. Anterior spinothalamic tract.
- It conveys.
- Crude touch
- Crude pressure
- Tactile localization.
2. Lateral spinothalamic tract.
- It carries
- Pain sensation
- Temperature sensation.

Question 4. Describe pyramidal tract with the help of diagram from origin to termination. (or) Draw and label pyramidal pathway.
Answer:
Pyramidal tract:
- These are descending tracts concerned with voluntary activities of the body.
- They are also called corticospinal tracts.
- They are two such tracts.
- Anterior corticospinal tract.
- Lateral corticospinal tract.
- The fibres of this tract arises from pyramid like structure in the medulla, thus they are called pyramidal tracts.
Origin:
- Fibers of pyramidal tract arises from following.

Course:
- The fibers of the pyramidal tract descend downwards, in diffused manner and then converge in the form of a fan like structure towards the brain stem as a radiating mass of fibers.
- This radiating mass is called corona radiata.
- Then, these fibers reach thalamus and descends down through.
1. Internal capsule:
- Here, it lie in the genu and anterior two-third of the posterior limb.
- Then, it enters mid-brain.
2. In midbrain:
- Here, it lie ventral to the substantia nigra.
3. In pons:
- Here, the fibers are broken up into a series.
- At the lower border of pons, the fibers are grouped once again.
4. In the medulla:
- The fibers occupies the most ventral part of the medulla.
- Here, the bundle of fibers gives an appearance of the pyramid.
- At the lower border of medulla, the pyramidal tract on each side is divided into 2 bundles of unequal sizes.
80% of fibers:
- Cross over and descend as the lateral corticospinal tract and end on the anterior horn cells.
- While crossing the midline, the fibers form the pyramidal decussation.
20% of fibers:
- Remain uncrossed
- Runs downwards in spinal cord as anterior corticospinal tract.
Termination:
- The fibers from both the tract terminate in the motor neurons of anterior grey horn.
- The axon of the anterior motor neurons leave the spinal cord as spinal nerves and supply the skeletal muscles.

Question 5. Describe origin, course and function of corticospinal. (or) Functions of pyramidal tract. tract.
Answer:
- Pyramidal tract is also called corticospinal tract.
Corticospinal Functions:
1. The pyramidal tracts are concerned with voluntary movement of the body.
- Lateral corticospinal tract.
- Convey motor impulses to control voluntary movements specially of the distal limb muscles.
- Concern with fine, precise movements.
- Anterior corticospinal tract.
- Convey motor impulses to control movements of trunk and proximal portions of the limb.
2. Forms part of pathway for superifcial reflexes
3. Fibers of this tract are concerned with sensory motor coordination.
Question 6. Describe the pain pathway. (or) Pathway of pain.
Answer:
- Lateral spinothalamic tract carries the pain sensation from the peripheral parts of the body to the CNS.
Pain Pathway Origin:
- Pain fibers arises from free nerve endings that are distributed throughout the body.
Pain Pathway Course:
1. First order neurons – posterior nerve root ganglia cells.
- Dendrites of these neurons receive the impulses and their axons carry them to the spinal cord.
- Fibers for fast pain.

2. Fibers for slow pain.

2. Second order neuron – marginal cells and substantia gelatinosa cells.
1. Fast pain.

2. Slow pain.
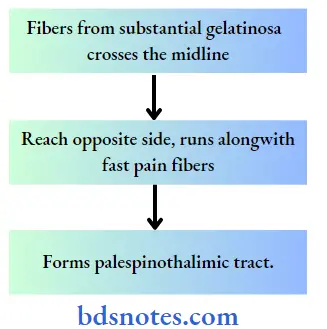

Pain Pathway Termination:
1. Fast pain fibers
- Majority of fibers terminate in ventral posterolateral nucleus of thalamus.
- Few fibers terminate in ascending reticular system of brainstem.
2. Slow pain fibers.
- One-fifth of fibers terminate in ventral posterolateral nucleus of thalamus.
- Remaining fibers terminate in either of the following.
- Reticular formation of brainstem.
- Tectum of midbrain
- Grey matter around aqueduct of sylvius.
- These terminating sites form third order neuron.
- Axons from these neurons reach the sensory area of the cerebral cortex.
Question 7. State the difference between upper motor neuron and lower motor neuron lesions.
Answer:

Question 10. Functional unit of nervous system.
Answer:
Neuron:
- The neuron is made up of.
1. Nerve cell body/soma:
- It is irregular in shape.
- It constitutes of
- Cytoplasm called neuroplasm. It contains.
- Nucleus.
- Large nucleus covers central part of the nerve cell body and has two or more nucleoli.
- Nissl granules/bodies.
- They are composed by many thin, parallely arranged, membrane bounded cavities.
- They are covered by minute particles containing RNA with proteins.
- Neurofibrils:
- They are thread like structures consisting of microfilaments and microtubules.
- Mitochondria and golgi apparatus.
- Nucleus.
- Cell membrane – covers neuroplasm:
- Cytoplasm called neuroplasm. It contains.
2. Dendrite:
- It is the branched process of the neuron.
- It transmits impulses towards nerve cell body.
- It contains nissl granules, mitochondira and neurofibrillae.

3. Axon:
- It originates from thickened area of the cell body called Avon Hillock.
- It is the longer process of the nerve cell.
- It conducts impulses away from the cell body
- The cytoplasmic fluid occupying the centre of the axon is called axoplasm.
- The cell membrane covering it is called axolemma.
- A short distance from its origin, the axon acquires myelin sheath.
- Axoplasm contains mitochondira, neurofibrils and axoplasmic vesicles but nissl bodies are absent.
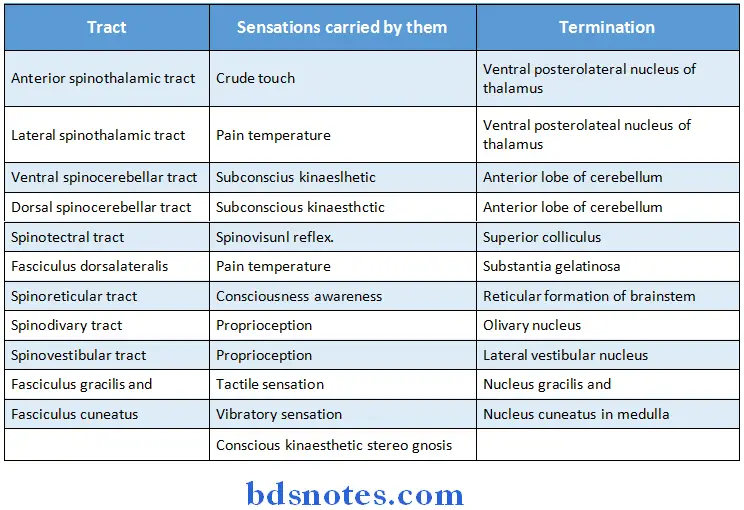
Question 11. Mention the names of the ascending tracts. Name the sensations carried by them and where will they terminate.
Answer:
Question 12. Name the descending tracts of thespinal cord. Trace the course of corticospinal tract.
Answer:
Descending tracts of the spinal cord:
1. Pyramidal tracts:
- Anterior corticospinal tract.
- Lateral corticospinal tract.
2. Extrapyramidal tracts:
- Medial longitudinal tract.
- Anterior vestibulospinal tract
- Lateral vestibulospinal tract
- Reticulospinal tract
- Tectospinal tract
- Rubrospinal tract
- Olivospinal tract.
Question 13. Cerebellum. (or) What are functional divisions of cerebellum? Give the functions of each division.
Answer:
- Cerebellum lies dorsal to the brain stem.
- On either side it is connected to brain stem by.
- Inferior cerebellar peduncle to the medulla.
- Middle cerebellar peduncle to the pons and.
- Superior cerebellar peduncle to the midrain.
Structure:
Cerebellum consist of.
1. A small medial portion called vermis.
- The part of vermis on the upper surface of cerebellum is called superior vermis.
- The part of vermis on the under surface of cerebellum is called inferior vermis.
- Vermis is formed by nine parts.
Fissures present over vermis:
- Primary fissure
- Prepyramidal fissure
- Posterolateral fissure.
2. Two large laterally placed cerebellar hemispheres.
- It has two portions.
- Larger portion called lobules ansiformis.
- Smaller portion called lobules paramedianus.
Functional division:
- Vestibulocerebellum.
- It receives impulses from vestibular apparatus
- Now, from vestibular apparatus afferent pass to vestibulocerebellum through vestibulocerebellar tract.
- Efferent return back to vestibular nuclei
- From these nuclei signals are send to spinal cord via vertibulospinal and reticulospinal tracts.
- Spino cerebellum.
- It regulates tone, posture and equilibrium by receiving impulses from proprioceptors in muscles, tendons, joints, tactile receptors, visual receptors and auditory receptors.
- It also receives the cortical impulses via pontic nuclei.
- It regulates postural reflexes by modifying muscle tone.
- It helps in adjustment of posture and equilibrium in response to visual and auditory pathway.
2. Control of muscle tone and stretch reflexes.
- Cerebellum forms an important site of a x y systems.
- The gamma motor neurons reflexly modify the activity of alpha motor neurons and thus regulate the muscle tone.
3. Control of movements.
- Involuntary movements.
- Cerebellum coordinates the subconscious movements.
- Voluntary movements.
- Cerebellum guides and controls all movements accompanied by a conscious awareness of an individuals.
Question 14. Parkinsonism.
Answer:
Parkinsonism Synonyms:
- Parkinson’s disease
- Paralysis agitans
- Shaking plasy.
- It is named after discoverer James Parkinson.
Parkinsonism Causes:
- Damage to basal ganglia.
- Viral infection of brain.
- Cerebral arteriosclerosis.
- Degeneration of dopaminergic nigrostriatal tract.
- Unknown cause called idiopathic parkinsonism.
Parkinsonism Features:
Age: Late middle age.
1. Rigidity:
- Affects mainly large proximal groups of muscles of limbs.
- Statue like state is produced.
- Limbs becomes more rigidity like pillars.
- This condition is called lead pipe rigidity.
2. Tremors:
- It consists of regular, rhythmic, alternate contraction of antagonist and agonist muscle.
- In parkinsonism, tremors occurs during rest thus called resting tremor.
- It increases in emotional states, anxiety, etc over first two fingers.
- This is known as “Pill-rolling” movement.
3. Akinesia and hypokinesia:
- Patient is unable to initial voluntary movements called akinesia. Hypokinesia means reduced voluntary movements.
4. Slow and monotonous speech.
5. Poverty of movements.
- It leads to
- Mask – like face
- Loss of normal subconscious associated movements.
- Shuffling gait patient walks quickly in short.
- Steps by bending forward.
6. Emotional changes:
- Patients are often emotionally upset.
Question 15. Functions of frontal lobe.
Answer:
1. Precentral cortex:
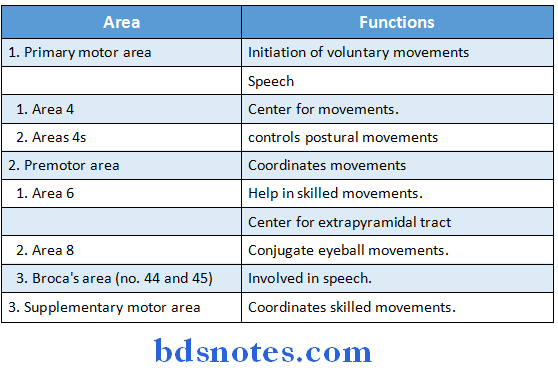
2. Prefrontal cortex:
Functions:
- Control of autonomic nervous system via. hypothalamus and brainstem.
- Control of some of the higher intellectual activities like learning, memory, reasoning, thinking.
- Control of personality
- Control of motions.
- Control of behaviour.
- Responsible for resting EEG.
- Centre for planned actions.
- Area is the seat of intelligence.
Question 16. Crerebrospinal fluid [CSF].
Answer:
- The fluid contained in the central canal of spinal cord, subarachnoid space and cerebral ventricles is known as cerebrospinal fluid.
Crerebrospinal fluid Properties:
- It is clear, color less, transparent, alkaline fluid.
- Specific gravity – 1,005 -1,008
- It is almost protein free and cell free
- Volume-130-150 ml.
- Dialy secretion – 500-550 ml.
- Rate of formation -0.2-0.3 ml/min.
- Pressure-average – 130 mm H2O in lying position, 200 mm in sitting position.
- pH – 7.33 (Alkaline)
- Osmolaity – 289 m Os ml kg/water
Crerebrospinal fluid Composition:
1. Water 99.13%
2. Solids 0.87%

Crerebrospinal fluid Formation:
- 50% by choroid plexuses in the ventricles.
- 40% by blood vessels of meningeal and ependymis lining of ventricles.
- 10% by blood vessels of brain and spinal cord.
Crerebrospinal fluid Circulation:

Crerebrospinal fluid Functions:
- Protective function – CSF acts as buffer and protects brain from shock.
- Acts as a reservoir to regulate the contents of cranium.
- Helps to transfer waste products of brain into blood.
- Serves as a medium for nutrient exchanges.
Question 17. What is lower motor neuron? What are the effects of lower motor neuron lesion?
Answer:
Lower motor neuron:
- Lower motor neuron are the anterior gray horn cells in the spinal cord and the motor neuron of the cranial nerve nuclei situated in brainstem which innervate the muscles directly.
Question 18. How are reflexes classified? What are the properties of a reflex?
Answer:
Classification of reflexes:
- Depending upon inborn or acquired
- Unconditional or inborn reflex
- Conditional or acquired reflex
- Depending upon the situation of the center
- Cerebellar reflex
- Cortical reflex
- Midbrain reflex
- Bulbar reflex
- Spinal reflex
- Depending upon the purpose
- Protective or flexor reflex
- Anti-gravity or extensor reflex
- Depending upon the number of synapse
- Monosynaptic
- Polysynaptic
- Depending upon clinical basis
- Superficial reflex
- Deep reflex
- Visceral reflex
- Pathological reflex
Question 19. Define reflex action and describe Babinski sign
Answer:
Reflex action:
- It is the response to a peripheral nervous stimulation that occurs without our consciousness.
Babinski’s sign:
- It is an abnormal plantar reflex
- It is elicited by a gentle scratch over the outer edge of the sole of the foot
- In normal plantar reflex it causes flexion and adduction of all toes
- In Babinski’s sign there is dorsiflexion of great toe and fanning of other toes
- It is present in
- Upper motor neuron lesion
- Infancy
- Deep sleep
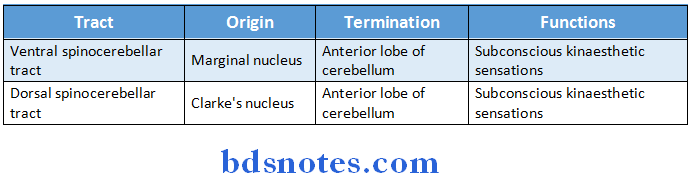
Question 20. Give the origin and termination of spinocerebellar tracts. Add a note on its functions.
Answer:
Question 21. What is saltatory conduction? Describe the classification of nerve fibres according to the rate of nerve conduction.
Answer:
Saltatory conduction:
- Myelin sheath is impermeable to ions
- Thus, sodium enter into nerve fibres from ECF only in the node of Ranvier and depolarisation occurs
- Depolarisation occurs in successive nodes and action potential thus, jumps from one node to another node
- This jumping is called saltatory conduction.
Classification of nerve fibres depending upon rate of conduction:
- Type A nerve fibres
- Type A alpha- conduction velocity is 70-120 m/sec
- Type A beta-conduction velocity is 30-40 m/sec
- Type A gamma – conduction velocity is 15-30 m/sec
- Type A delta – conduction velocity is 12-30 m/sec
- Type B nerve fibres – conduction velocity is 3-20 m/sec
- Type C nerve fibres
- Subtype 1-conduction velocity is 0.5-2 m/sec
- Subtype 2-conduction velocity is 0.7-2.3 m/sec
Question 22. Neuron.
Answer:
Neuron Definition:
- Neuron is defined as structural and functional unit of the nervous system.
Neuron Classification:
1. Depending upon the number of poles.
- Unipolar neurons
- Bipolar neurons
- Multipolar neurons.
2. Depending upon the functions.
- Motor neurons
- Sensory neurons.
3. Depending upon length of axon.
- Golgi type I neuron – Have ong axons.
- Golgi type II neuron – Have short axons.
Neuron Structure:
- Neuron is made up of
- Nerve cell body
- Axons
- Dendrite
Neuron Functions:
- Nerve cell body – maintains functional and anatomical integrity of axon.
- Dendrite transmits impulses towards cell body.
- Axon – transmits impulses way from cell body.
Question 23. Types of nerve fibers.
Answer:
1. Depending upon structure.
- Myelinated nerve fibers.
- Nerve fibers covered by myelin sheath.
- Non myelinated nerve fibers.
- Does not have myelin sheath.
2. Depending upon distribution.
- Somatic nerve fibers – supplies skeletal muscles.
- Visceral nerver fibers – supplies internal organs of body.
3. Depending upon origin.
- Cranial nerves – arises from the brain.
- Spinal nerves – arises from spinal cord.
4. Depending upon function.
- Motor nerve fibers – carries motor impulses.
- Sensory nerve fibers – carries sensory impulses.
5. Depending, upon secretion of neurotransmitter.
- Adrenergic nerve fibers – secretes noradrenaline.
- Chlonergic nerve fibers – secretes acetylcholine.
6. Depending upon diameter and conduction.
- Type A
- Type B
- Type C.
Question 24. Conduction of impulses in myelinated nerve fibers/saltatory conduction.
Answer:
Node of Ranvier:
- It is a part of nerve fiber which is not covered by myelin sheath.
Saltatory conduction:
- Myelin sheath is impermeable to ions.
- Thus, sodium enter into nerve fibers from ECF only in the node of Ranvier and depolarization occurs.
- Depolarization occurs in successive nodes and action potential thus, jumps from one node to another node.
- This jumping is called saltatory conduction.
Question 25. Name any four mechanoreceptors.
Answer:
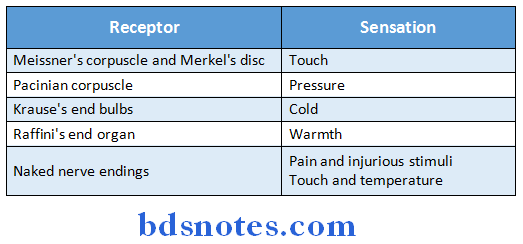
Question 26. Types of synapse.
Answer:
1. Anatomical classification:
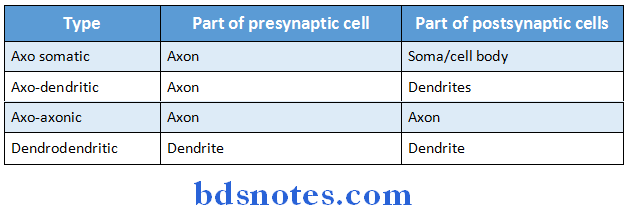
2. Functional classification:
- Based on transmission of impulses.
- Electrical synapse
- Chemical synapse.

Question 27. Synpatic transmission. (or) Trace the lateral spinothalamic tract
Answer:
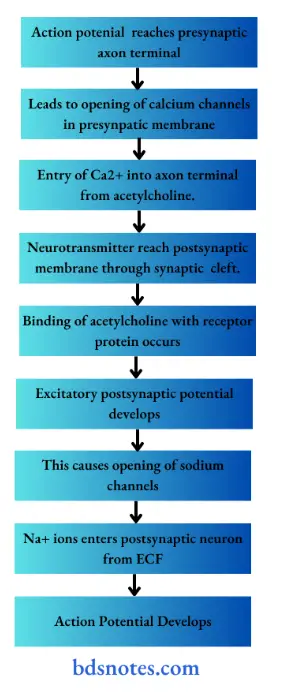
Question 28. Define reflex and write about reflex activity.
Answer:
Reflex:
- It is an involuntary response to a stimulus which depends on integrity of reflex pathway.
Reflex activity:
- It is a type of protective mechanism.
- It protects the body from irreparable damages.
Examples:
1. When hand is placed one a hot object, it is withdrawn immediately.
2. When a very bright light is thrown into the eyes, eyelids are closed and pupils are constricted.
- This prevents damage to retina.
Question 29. Lower motor neuron.
Answer:
- Lower motor neuron are the anterior grey horn cells in the spinal cord and the motor neurons of the cranial nerve nuclei situated in brainstem.
- They innervate the muscles directly.
- They constitute the final common pathway of motor system.
- Its action is under the influence of the upper motor neurons.
Lower motor neuron Types:
1. Alpha motor neuron.
- Innervates extrafusal fibers of muscles and causes contraction of muscles.
2. Gamma motor neuron.
- Innervates intrafusal fibers of muscles and maintains the muscle tone.
Question 30. Refered pain.
Answer:
Refered pain Definition:
- When the sensation of pain is experienced at the site other than the injured or diseased part is called referred pain.
- Deep pain are referred but not the superficial pain.
Refered pain Mechanism:
- Dermatomal rule – pain is referred to a structure which is developed from the same dermatome from which the pain producing structure is developed.
Refered pain Examples:
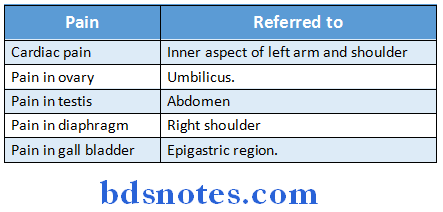
Question 31. Pathway of pain.
Answer:

Question 32. Hypothalamus.
Answer:
- Hypothalamus is a part of diencephalon.
- It lies below the thalamus and forms the floor and inferior part of the lateral walls of the 3rd ventricles.
Hypothalamus Functions:
- Secretion of pituitary hormones.
- Control of adrenal gland.
- Regulation of ANS.
- Regulation of heart rate and blood pressure
- Thermoregulation.
- Control of hunger and feeding
- Control of water balance.
- Role in biological clock.
- Control of waking-sleep cycle.
- Control of emotions.
- Regulation of sexual function.
- Regulation of response to smell.
Question 33. Functions of cerebellum.
Answer:
- Regulation of body posture and equilibrium.
- Control of muscle tone and stretch reflexes. Coordination of movements.
- Regulation of automatic associated movements.
- Regulates movements of extraocular muscles.
Question 34. EEG [Electroencephalogram]
Answer:
Electroencephalogram Definition:
- The recording of electrical activities of brain is called electroencephalogram (EEG).
Electroencephalogram Significance:
- EEG helps in diagnosis of sleep disorders and neurological disorders like.
- Epilepsy
- Disorders of midbrain.
- Subdural hematoma.
Electroencephalogram Waves:
- Alpha rhythm.
- Beta rhythm.
- Delta rhythm.
Question 35. Sleep.
Answer:
Sleep Definition:
- The mental and physical relaxation either superifically or deeply with closed eyes in known as sleep.
Sleep Types:
1. Rapid eye movement sleep.
- Rapid conjugate eye movements occurs frequently.
- Dreams occurs during this period.
- Occupies 20-30% of sleep.
- This sleep is deep sleep.
- It plays an important role in consolidation of memory.
2. Non-rapid eye movement sleep.
- Eyeballs donot move.
- Dreams donot occur.
- Occupies 70-80% of sleep.
- It is followed by rapid eye movement sleep.
Question 36. Epilepsy.
Answer:
Epilepsy Definition:
- It is a brain disorder characterized by convulsive seizures or loss of consciousness or both.
Epilepsy Cause:
- Paroxysmal uncontrolled discharge of impulses from neurons of brain.
Epilepsy Types:
1. Generalized epilepsy.
Epilepsy Cause:
- Excessive discharge of impulses from all parts of brain.
Epilepsy Subtypes:
- Grand mal.
- Petit mal
- Psychomotor epilepsy.
2. Localized epilepsy.
Localized Epilepsy Cause:
- Excessive discharge of impulses from one part of brain.
Question 37. Lumbar puncture.
Answer:
- It is method of collection of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).
- In it, the lumbar puncture needle is introduced into the subarachnoid space in the lumbar region between the third and fourth lumbar spines.
Lumbar puncture Method:

Lumbar puncture Uses:
- For diagnosis
- For determining pressure exerted by CSF
- For introducing spinal anaesthesia.
Question 38. Autonomic nervous system (ANS).
Answer:
- Autonomic nervous system is primarily concerned with the regulation of visceral functions of the body.
Autonomic nervous system Division:
- Sympathetic
- Parasympathetic.

Question 39. Discuss two properties of synapse.
Answer:
Properties of synapse:
- One way conduction – Bell Magendie Law
- The impulses are transmitted only in one direction from pre synaptic neuron to post synaptic neuron
- Synaptic delay
- A short delay occurs during transmission of impulses in synapse
- Fatigue
- The synapse forms a seat of fatigue along with the Betz cells.
Question 40. State four functions of thalamus.
Answer:
Functions of thalamus:
- Relay center for sensations
- Center for
- Processing sensations
- Determining nature of sensations
- Sexual sensation
- Reflex activity
- Alertness
- Integration of motor activity
Question 41. Name the ascending tracts of the spinal cord.
Answer:
Ascending tracts:
- Anterior spinothalamic tract Lateral spinothalamic tract
- Ventral spinocerebellar tract
- Dorsal spinocerebellar tract
- Spinotectal tract
- Fasciculus dorsolateralis
- Spinoreticular tract
- Spinoolivary tract
- Spinovestibular tract
- Fasciculus gracilis
- Fasciculus cuneatus
Question 42. Name the ascending tract conducting
1. Crude touch
2. Fine touch
Answer:

Question 43. Give the function of thalamus.
Answer:
Functions of thalamus:
- Relay center for sensations
- Center for
- Processing sensations
- Determining nature of sensations
- Sexual sensation
- Reflex activity
- Alertness
- Integration of motor activity
Question 44. Name one descending tract in the spinal cord and give its function.
Answer:

Question 45. List four signs of Parkinson’s disease.
Answer:
Signs of Parkinson’s disease:
- Static or resting tremor occurs
- Slowing down of movement
- Loss of automatic associate movement
- Stiffness of muscle
- Festinant gait
- Emotionally upset
- Dementia
Question 46. Name types of neuroglia. What are their functions?
Answer:
Neuroglia:

Question 47. Broca’s area.
Answer:
- Broca’s area is the motor area for speech
- It is present in left hemisphere of right handed persons and in right hemisphere of left handed persons
- It is a special region of premotor cortex situated in inferior frontal gyrus
- It is responsible for movement of tongue, lips and larynx which are involved in speech.
Question 48. Name three ascending tracts and specify what sensation is carried by each of them.
Answer:
Ascending tracts:
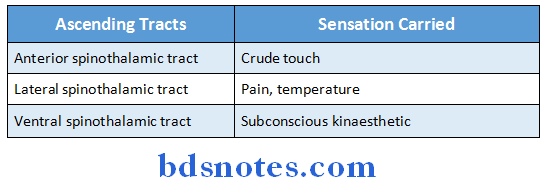
Question 49. Give any two features of cerebellar lesion.
Answer:
Features of cerebellar lesions:
- Atonia- loss of muscle tone or hypotonia – reduction in tone occurs
- Lateral deviation of arms when both the arms are stretched and held in front of the body with closed eyes
- Pendular movement occurs on eliciting tendon jerk.

Leave a Reply