Cardiac Glycosides And Drugs For Heart Failure
Question 1. Enumerate Important Indications Contraindications And Adverse Reactions Of Digitalis.
Or
Write Important Uses, Side Effects, And Contraindications Of Digitalis.
Or
Give An Account Of Adverse Reactions To Digitalis.
Or
Describe The Therapeutic Uses Of Digoxin.
Answer:
Indications Or Uses Of Digitalis
- It is used in the treatment of congestive heart failure.
- It is used in the treatment of cardiac arrhythmias.
- In atrial fibrillation, it controls the ventricular rate by reducing the number of impulses passing down to the AV node.
- During atrial flutter, it decreases ventricular rate.
- It is used in paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia.
Read And Learn More: Pharmacology Question And Answers
Contraindications Of Digitalis
- During treatment with digitalis partial AV block is converted to complete AV block.
- The use of digitalis in myocardial infarction may produce arrhythmias.
- It causes hypokalemia.
- It causes ventricular tachycardia.
Adverse Reactions Or Side Effects Of Digitalis
Adverse effects of digitalis are divided into two parts i.e. ext- extracardiac and cardiac.
Extracardiac Side Effects
- GIT: Anorexia, nausea, and vomiting.
- CNS: Headache, confusion, restlessness, disorientation, weakness, altered mood, and hallucination.
- Skin rashes and gynecomastia.
Cardiac Side Effects
It can produce any type of arrhythmia. It can cause AV block, atrial tachycardia, atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter, and bradycardia.
Question 2. Explain Why Iv Calcium Should Not Be Given To Patients On Digitalis Therapy?
Answer:
When IV calcium is given to a patient on digitalis therapy it synergizes with digitalis and precipitates digitalis toxicity. That’s why IV calcium should not be given to patients on digitalis therapy.
Question 3. Write The Basic Use Of Potassium Sparing Diuretics In Congestive Heart Failure.
Answer:
The potassium diuretics cause:
- Decrease preload and improve ventricular efficiency by reducing circulating volume.
Removeperipheraledemaandpulmonarycongestion. - IV furosemide promptly increases the systemic venous capacitance and produces rapid symptomatic relief.
- That’s why potassium-sparing diuretics are used in congestive heart failure.
Question 4. Write The Basic Use Of Vasodilators In Chf.
Answer:
Vasodilators are one of the important drugs used in CHF. Mainly they are of three types based on their classification.
- Arterial dilators decrease afterload, i.e. hydralazine and nifedipine.
- Vasodilators decrease preload, i.e. glycerine trinitrate.
- Mixed dilators cause a decrease in pre- and afterload, i.e. ACE inhibitors and losartan.
They are used IV to treat acute heart failure that occurs in advanced cases and orally for long-term therapy of chronic congestive cardiac failure. They mainly act by:
- Preload reduction
- Afterload reduction
- Pre- and afterload reduction.
Question 5. Explain Why Thiazide Diuretics Are Not To Be Used With Digoxin In The Treatment Of Congestive Heart Failure?
Answer:
Since thiazide diuretics promote the release of aldosterone which causes compensatory sodium retention and potassium loss leading to hypokalemia.
As digoxin leads to the inhibition of sodium-potassium ATPase and causes depletion of potassium. The thiazide diuretics enhance digitalis toxicity and cause cardiac irregularities.
Question 6. Explain why digoxin is given in atrial fibrillation.
Answer:
Atrial fibrillation is a condition in which the heart rate is more than 350 beats per minute. The high number of impulses generated in the atria is transmitted to the ventricles resulting in an increase in ventricular rate.
At such high rates, the ventricles do not get the time to completely contract leading to ineffective ventricular contractions (ventricles contract but cannot pump blood properly). This may be fatal for the individual.
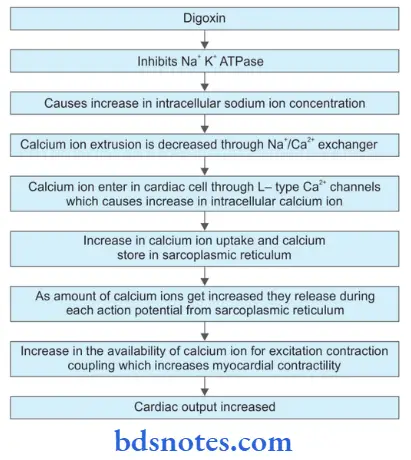
For this condition, we need to either convert the atrial fibrillation to sinus rhythm or at least control the ventricular rate (achieved with digitalis). The mechanism of action of digoxin is as follows:
- Digoxin has a vagomimetic action due to which it increases the effective refractory period (ERP) of 96 Mastering the BDS IInd Year (Last 25 Years Solved Questions) Pharmacology AV node. Thus, the number of impulses which are
able to pass down the AV node to the ventricles is significantly reduced. - The vagomimetic action of digoxin also reduces the refractory period of the atria leading to an increased frequency of atrial contractions. The increased number of impulses hitting the AV node makes the AV node refractory for the subsequent impulses. Thus, less number of impulses can be transmitted to the ventricles.
- The reduction in the number of impulses reaching the ventricles reduces the ventricular rate leading to more effective contractions i.e. ventricles can contract more strongly increasing the cardiac output.
Question 7. Mention Different Groups Of Drugs In Congestive Cardiac Failure And Explain Their Mechanism Of Action.
Answer:
Drugs In Congestive Cardiac
Failure There are two distinct goals of drug therapy in congestive heart failure:
- Relief of congestive/low output symptoms and restoration of cardiac performance. Drugs used are:
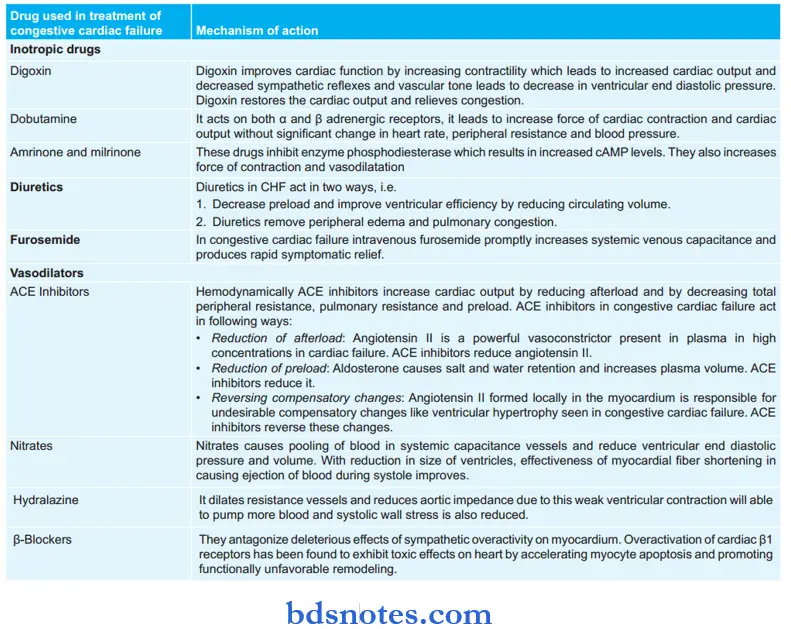
- Inotropic Drugs: Digoxin, dobutamine and amrinone, milrinone
- Diuretics: Furosemide, thiazide
- Vasodilators: ACE inhibitors, angiotensin antagonists, hydralazine, nitrate, nitroprusside
- β blockers: Metoprolol, bisoprolol, carvedilol.
- Arrest/reversal of disease progression and prolongation of survival:
- ACE inhibitors/Angiotensin antagonist
- β blockers
- Aldosterone antagonist: Spirinolactone
Mechanism Of Action Of Drugs Used In Treatment Of Congestive Cardiac Failure (See Table):

Question 8. Classify The Drugs Used In The Treatment Of Heart Failure. Describe The Mechanism Of Action.
Answer:
Drugs Used In The Treatment Of Heart Failure
There are two distinct goals of drug therapy in congestive heart failure:
- Relief of congestive/low output symptoms and restoration of cardiac performance. Drugs used are:
- Inotropic drugs: Digoxin, dobutamine and amrinone, milrinone
- Diuretics: Furosemide, thiazide
- Vasodilators: ACE inhibitors, angiotensin antagonists, hydralazine, nitrate, nitroprusside
- β blockers: Metoprolol, bisoprolol, carvedilol.
- Arrest/reversal of disease progression and prolongation of survival:
- ACE inhibitors/angiotensin antagonist
- β blockers
- Aldosterone antagonist: Spirinolactone.
Digoxin Mechanism Of Action

Leave a Reply