Review of Literature
Question 1. Definition Of Review Of Literature
Answer:
The review of literature is defined as a broad, comprehensive in-depth, systematic, and critical review of scholarly publications, unpublished scholarly print materials, audiovisual material, and personal communications.
According To Virginia Cano:
- A review of literature is a critical summary and an assessment of the current state of knowledge or current state of the art in a particular field.
According To Chris Jordan:
- A review of literature is the selection of available documents (both published and unpublished) on the topic, which contains information, ideas, data, and evidence written from a particular standpoint to fulfill certain aims or to express certain views on the nature of the topic and how it is to be investigated, and the effective evaluation of these documents in relation to the research being proposed.
Read And Learn More: BSc Nursing 3rd Year Nursing Research And Statistics Previous year Question And Answers
Question 2. Purposes Of Literature Review
Answer:
- The review of literature is defined as a broad, comprehensive in-depth, systematic, and critical review of scholarly publications, unpublished scholarly print materials, audiovisual material, and personal communications.
According To Virginia Cano:
- A review of literature is a critical summary and an assessment of the current state of knowledge or current state of the art in a particular field.
- Research is an ongoing process that builds on previous knowledge. There are very few topics so rare that have never been investigated.
There are many purposes for reviewing the literature before conducting a research study.
- Identification of a research problem and development or refinement of research question or hypothesis
- To demonstrate familiarity with a body of knowledge and to establish credibility.
- To show the path of prior research and how a current project is linked to it.
- To integrate and summarize what is known in an area.
- To learn from others and stimulate new ideas.
- Orientation to what is known and not known about an area of inquiry, to ascertain what research can best make a contribution to the existing base of evidence.
- Determination of any gap or inconsistencies in a body of research.
- Determination of a need to replicate a prior study in a different setting or with a different study population.
- Identification or development of new or refined clinical interventions to test through empirical research.
- Identification of relevant theoretical or conceptual for a research problem.
- Identification of suitable designs and data collection methods for a study.
- For those developing research proposals for funding, identification of experts in the field who could be used as consultants.
- Assistance in interpreting study findings and in developing implications and recommendations.

Question 3. Explain Sources Of The Literature Review
Answer:
- The types of information sources for a review of literature are conceptual and data-based literature.
- The common sources of both these literature are books, chapters of books, journal articles, abstracts, critique reviews, abstracts published in conference proceedings, professional and governmental reports, and unpublished doctoral dissertations and theses.
The Kinds Of Information Available In Written Documents Can Be Categorized Into Five Broad Classes:
- Facts, findings, or results.
- Theory.
- Research procedure or methods.
- Opinions, points of view, or personal commentaries.
- Anecdotes or impressions on a particular event or situation.
The references can be categorized as being either primary or secondary sources.
Primary Sources:
- A primary source is written by a person. Who developed the theory or conducted the research or is the description of an investigation written by the person who conducted it
- Most primary sources are found in published literature, e.g. nursing research articles. A credible literature review reflects the use of mainly primary sources.
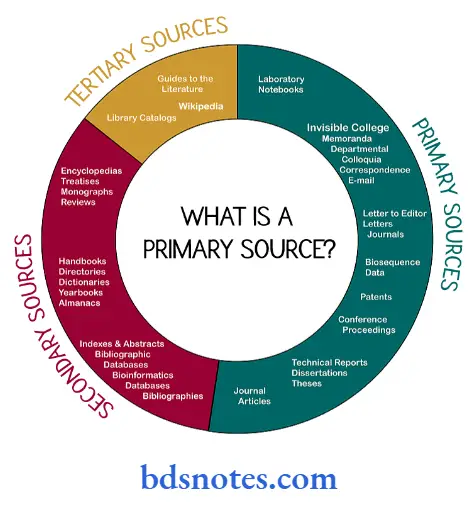
Secondary Sources:
- A secondary source is written by persons other than the individual who developed the theory or conducted research.
- Otherwise, known as it is a description of a study or studies prepared by someone other than the original researcher.
- Often secondary source represents a response to, or a summary and critique of a theorist or researcher’s work.
- Secondary sources may be used when unavailability of primary sources, and if we want to know different ways of looking at an issue or problem.
Question 4. Steps in Review of Literature
Answer:
The preliminary review generally includes three steps:
- Identification of important publications-earlier works, reports, recent publications-Journals books Medlars, Medline Cat-line.
- Summarize and record the contents of the publication contents-such as theoretical perspective, definitions, research design
- Comparison of content such as theoretical perspectives, definitions, research, design, methods, instruments, and findings
Way To Review:
1. To select pertinent books or articles from a general review of the literature, examine the book or article quickly.
- For a book, examine the title page that gives the author credentials then scan the table of contents, the index, the bibliography, and the charts and table.
- Read the preface rapidly to determine the author’s purpose; then thumb through the chapters quickly to assess substance.
- If the book is promising, keep it for a critical review. For the article, examine the author’s credentials, quickly scan the problem statement, and the hypotheses, and then focus on the methods of research used, especially how the sample was selected and the data analyzed.
- Read the conclusion and summaries and note the use of theory and other research studies. Retain sound and pertinent literature for summary and critique.
2. To summarise and record information, first note the author, title of the article, and year of publication. If further information is needed, this immediately refers to the reader to the bibliography card.
3. Record information from a research report in the following order(s):
- Problem statement
- Definition of concepts
- Hypothesis if any
- Theories or assumptions used
- Method of research including how samples were drawn
- Instruments and scales used
- Type of research (description or explanation)
- Methods and findings of data analysis
- Interpretations of data especially whether the hypothesis is supported or rejected
- Recommendations and suggestions for further research if any
- Make special note of implications for nursing practice or theory.
4. Note that data was not included, such as limitations that were not noted, means of establishing the validity and reliability of instruments that were not given, theory that was not used, or former studies that were not examined.
- Comparison of the recorded summaries of literature enables the researcher to contrast definitions of concepts, uncover competing theories used to explain the same phenomenon,
- Consider the various designs that have been utilized to study the same problem, examine different methods of data collection, and find valid instruments already developed.

Leave a Reply