Immunochemistry
Question 1.Structure and classification of immunoglobulins.
Answer.
Definition Of Immunoglobulin
Immunoglobulins are a family of serum proteins, which function as antibodies
Classification Of Immunoglobulin
Immunoglobulins are classified into 5 types:
- IgG
- IgM
- IgA
- IgD
- IgE
Structure Of Immunoglobulin
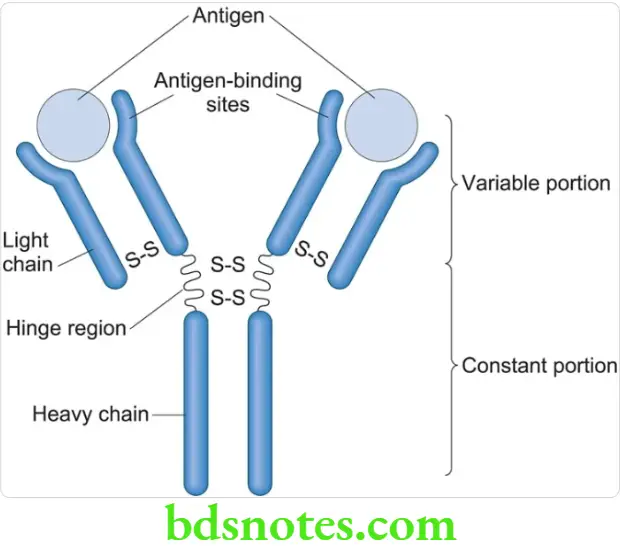
- The structure of immunoglobulin is known as the Edelman Gally model
- Immunoglobulins are Y shaped
- Each molecule has 2 heavy chains (H chains) and 2 light chains (L chains) – H2L2
- The chains are held together by inter-chain disulphide bridges to form a bilaterally symmetric structure
- Each chain is made up of a number of loops or domains of a constant size (100 amino acids)
- The N terminal domain of each chain shows more variation and is known as the variable region or V region
- The C terminal domain is relatively constant and is known as the constant region or C region
- The zone where the variable and constant regions join is known as the switch region
- The region of the H chain which is more susceptible to proteolytic attack and is more flexible, is known as the hinge region
- The antibody binding site is known as the Fab region
- The complement fixing site is known as the Fc region
Read And Learn More: BSc Nursing 1st Year Nutrition And Biochemistry Previous year Question and Answers
Question 2. Classify immunoglobulins and write one function of each class.
Answer.
Definition Of Immunoglobulin
Immunoglobulins are a family of serum proteins, which function as antibodies
Classification Of Immunoglobulin
Immunoglobulins are classified into 5 types:
- IgG
- IgM
- IgA
- IgD
- IgE
1. IgG
- IgG comprises 70 to 80 % of the total immunoglobulins
- Its serum level is 1200 mg %
- It is a glycoprotein
- The synthetic rate of IgG is 36 mg/kg/day
Function of IgG
IgG is the only immunoglobulin that can cross the placenta freely and is responsible for the protection of newborns during the first few months of life
On antigenic stimulation IgM is produced initially, followed later and ultimately replaced by IgG
2. IgM
- IgM constitutes 7 % of the total immunoglobulins
- Serum level of IgM is 100 mg %
- It is a glycoprotein
- IgM is a pentamer and has a J chain (joining chain)
Function of IgM
IgM it is the first antibody to appear in responce to initial exposure to an antigen.
3. IgA
- IgA accounts for 10 to 20 % of the total immunoglobulins
- The normal serum level of IgA is 200 mg %
- It is a glycoprotein
- IgA contains the J chain
Function of IgA
IgA provides the primary defence mechanism against local infections
IgA prevents access of foreign substances to the general immunologic system
4. IgD
- IgD forms 0.2 % of the total immunoglobulins
- Its serum concentration is 3 mg %
- IgD is easily degraded by heat and proteolytic enzymes
Function of IgD
- IgD is the predominant immunoglobulin on the surface of B lymphocytes and may be involved in the differentiation of these cells
- IgD has antibody activity towards
- Penicillin
- Milk proteins
- Insulin
- Diphtheria toxin
- Thyroid antigen
5. IgE
- IgE comprises 0.004 % of the total immunoglobulins
- Its serum level is 10 to 70 micrograms %
- IgE binds to certain specific antigens known as allergens
Function Of IgE
IgE can fix to leucocytes and release mediators of inflammation on exposure to allergens. Thus IgE plays an important role in response of the individual in allergies.

Leave a Reply