Composition And Metabolism Of Carbohydrates
Question 1.Classify carbohydrates with suitable examples.
Answer.
Definition Of Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates may be defined as polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones or compounds which produce them on hydrolysis
Classification Of Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are classified into 3 groups:
- Monosaccharides
- Oligosaccharides
- Diasaccharides
- Polysaccharides
Monosaccharides
- Monosaccharides are the simplest group of carbohydrates and are referred to as simple sugars
- They cannot be further hydrolysed
- The monosaccharides are divided into different categories depending on the functional group and the number of carbon atoms
- When the functional group in monosaccharides is an aldehyde, they are known as aldoses e.g. glyceraldehyde, glucose
- When the functional group is a keto group, they are known as ketoses e.g. dihydroxyacetone, fructose
- Based on the number of carbon atoms, the monosaccharides are regarded as trioses (3C), tetroses (4C), pentoses (5C), hexoses (6C) and heptoses (7C).
Oligosaccharides
- Oligosaccharides contain 2 to 10 monosaccharide molecules which are liberated on hydrolysis
- Based on the number of monosaccharide units present the oligosaccharides are further subdivided as –
- Disaccharides (2) – e.g. Maltose
- Trisaccharides (3) – e.g. Raffinose
- Tetrasaccharides (4) – e.g. Stachyose
- Pentasaccharides (5) – e.g. Fondaparinux
Disaccharides
- Disaccharides are sugars which yield two molecules of the same or different molecules of monosaccharides on hydrolysis e.g. maltose, lactose and sucrose
- Maltose yields two molecules of glucose on hydrolysis
- Lactose yields one molecule of glucose and one molecule of galactose on hydrolysis
- Sucrose yields one molecule of glucose and one molecule of fructose on hydrolysis
Polysaccharides
- Polysaccharides are sugars which yield more than ten molecules of monosaccharides on hydrolysis
- They are of two types
- Homo-polysaccharides – they are polymers of the same monosaccharide units e.g. – starch, glycogen, inulin, dextrin, dextran and cellulose
- Hetero-polysaccharides – they are polymers of different monosaccharide units or their derivatives.
They are also known as mucopolysaccharides or glycosaminoglycans (GAGS) e.g. – keratan sulfate, chondroitin sulfate, heparin and hyaluronic acid
Question 2. Write Down The Functions Of Carbohydrates.
Answer.
Functions Of Carbohydrates
- Carbohydrates are the most abundant dietary source of energy (4 C/gm)
- Carbohydrates are the precursors for many organic compounds such as fats and amino acids
- Carbohydrates participate in the structure of cell membrane
- Carbohydrates play a role in cellular functions such as cell growth, adhesion and fertilization
- Carbohydrates serve as the storage form of energy (glycogen) to meet the immediate energy demands of the body
- Carbohydrate derivatives are used as drugs e.g. cardiac glycosides and antibiotics
- Lactose is the principal sugar of milk in the lactating mammary gland
- Carbohydrates are constituents of compound lipids and conjugated proteins
- Heparin is an anti-coagulant
- Hetero-polysaccharides form the ground substance of tissues
Question 3. Factors regulating blood sugar level.
Answer.
Regulation Of Blood Glucose Level
Blood glucose level is regulated by the following hormones:
- Insulin
- Glucocorticoids
- Growth hormone
- ACTH
- Epinephrine
- Glucagon
- Thyroid hormones
Insulin
Insulin is secreted from the beta cells of the pancreas.
Insulin decreases blood glucose level by
- It decreases the delivery of glucose from the liver to the blood
- It increase glycolysis
- It increases glycogenesis
- It decreases glycogenolysis
- It decreases gluconeogenesis
Glucocorticoids
Glucocorticoids are secreted from the adrenal cortex
Glucocorticoids increase blood glucose level by:
- They increase protein catabolism in the peripheral tissues and the amino acids formed are used for gluconeogenesis
- They decrease the peripheral uptake of glucose
- They decrease glycolysis
- They increase gluconeogenesis
Growth Hormone
Growth hormone is secreted from the anterior pituitary gland
Growth hormone increases the blood glucose level by:
- It decreases the glucose uptake by certain tissues e.g. muscles
- It increases gluconeogenesis
ACTH
Adreno cortico tropic hormone (ACTH) is secreted from the anterior pituitary gland
It increases the blood glucose level by:
- It increases the secretion of glucocorticoids
- It increases gluconeogenesis
Epinephrine
Epinephrine is secreted from the adrenal medulla
Epinephrine increases the blood glucose level by:
- It increases glycogenolysis in the liver and muscles
- It increases ACTH formation
- It increases gluconeogenesis
- It inhibits the release of insulin from the pancreas
Glucagon
Glucagon is secreted from the alpha cells of the pancreas
Glucagon increases blood glucose level by:
- It increases glycogenolysis in the liver
- It increases gluconeogenesis
Thyroid Hormones
Thyroid hormone (T3 and T4) are secreted from the thyroid gland
They increase the blood glucose level by:
- They cause destruction of insulin
- They increase the absorption of glucose from the intestine
- They increase gluconeogenesis
- They increase protein catabolism in the peripheral tissues and the amino acids formed are used for gluconeogenesis
- They increase glycogenolysis
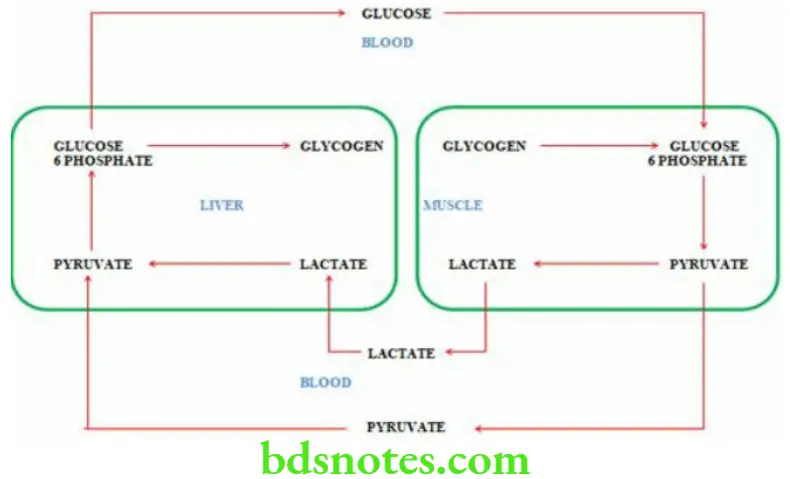
Question 4. Explain Cori’s cycle.
Answer.
Cori’S Cycle
- Muscles cannot convert glucose 6 phosphate to glucose due to absence of the enzyme glucose 6 phosphatase
- Lactate formed in the muscles enters the blood and is carried to the liver where it is converted to glucose by gluconeogenesis
- The glucose thus formed then enters the muscles
- This cycle is called Cori’s cycle
Question 5. Describe the steps of TCA cycle. Add a note on its energetics.
Answer.
Characteristic Features Of KREBS Cycle
- Krebs cycle is also known as the citric acid cycle or tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA cycle)
- It is the final common pathway for the breakdown of carbohydrates, lipids and proteins
- It takes place in the mitochondrial matrix
- It takes place only in the presence of oxygen (aerobic conditions)
- Absence of oxygen (anoxia) or partial deficiency of oxygen (hypoxia) causes total or partial inhibition of the cycle
- NADH and FADH2 formed in the Krebs cycle enter the electron transport chain and generate ATP’s
- Intermediates of Krebs cycle play a role in the synthesis of many important compounds such as non-essential amino acids, fatty acids, haeme, cholesterol and steroids.
Reactions Of KREBS Cycle
- Krebs cycle takes place in the mitochondria
- Oxaloacetate combines with acetyl COA to form citrate in the first step of Krebs cycle
- Citrate then undergoes a series of reactions to regenerate oxaloacetet
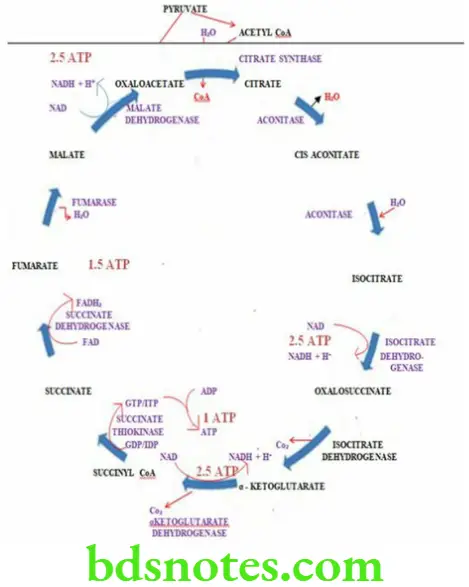
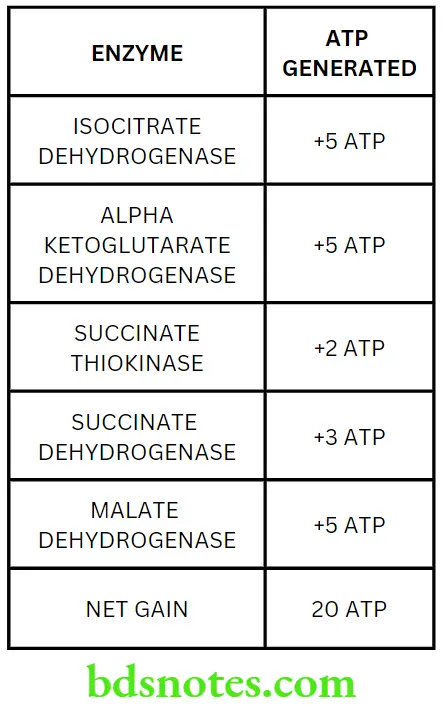
Read And Learn More: BSc Nursing 1st Year Nutrition And Biochemistry Previous year Question and Answers
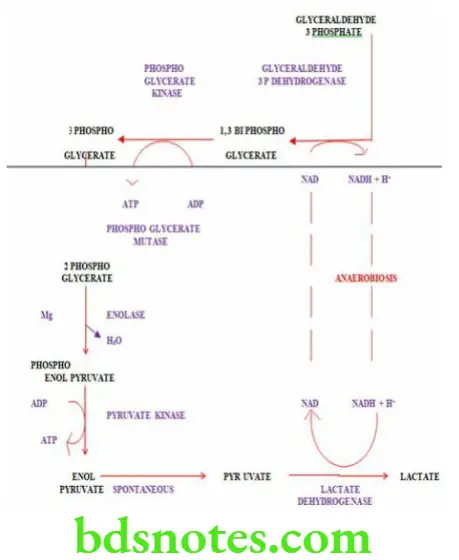
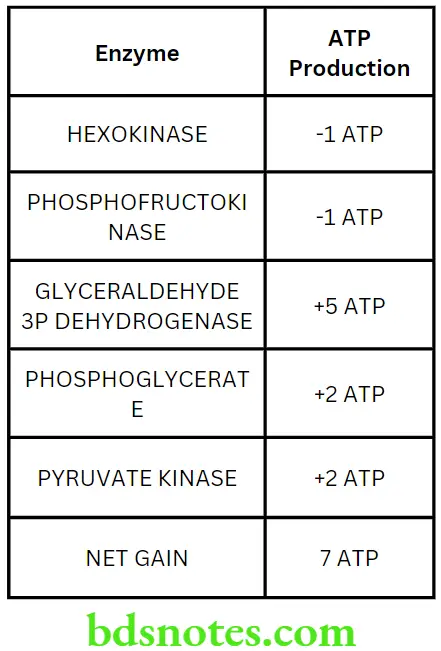
Question 6. Explain glycolysis in detail with its energetics.
Answer.
Glycolysis Definition
The oxidation of glucose to pyruvate and lactate is called glycolysis
Characteristic Features Of Glycolysis
- It is meant for the provision of energy
- It is also called Embden Meyerhof Parnas (EMP) pathway
- It occurs in all the tissues
- Erythrocytes and brain derive energy mainly from glycolysis.
- It can take place in both aerobic and anaerobic conditions.
- Glycolysis takes place in the cytoplasm of the cell
- It is important in skeletal muscles as glycolysis provides ATP even in the absence of oxygen, hence muscles can survive anoxic episodes
- In fast growing cancer cells the rate of glycolysis is very high leading to the accumulation of lactic acid, causing acidosis. The local acid environment is helpful in cancer therapy
- Deficiency of certain enzymes (hexokinase and pyruvate kinase) of glycolysis can cause haemolytic anaemia.
Reactions Of Glycolysis
- Glucose is freely permeable to liver cells
- In the intestinal mucosa and kidney tubules glucose is taken up by active transport
- In other tissues such as skeletal muscles, cardiac muscle, diaphragm and adipose tissue insulin facilitates the uptake of glucose
- In aerobic conditions glucose is oxidized to pyruvic acid and in anaerobic conditions it is oxidized to lactic acid.
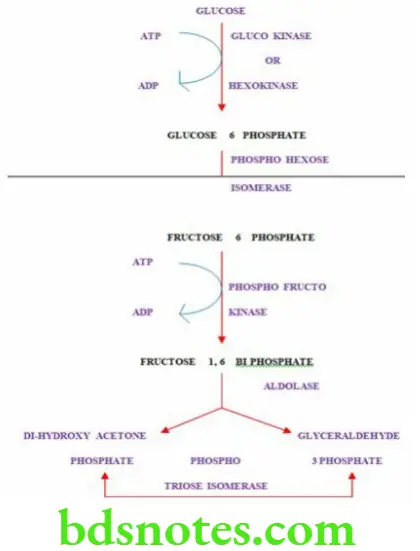
Question 7. Glycogenesis.
Answer.
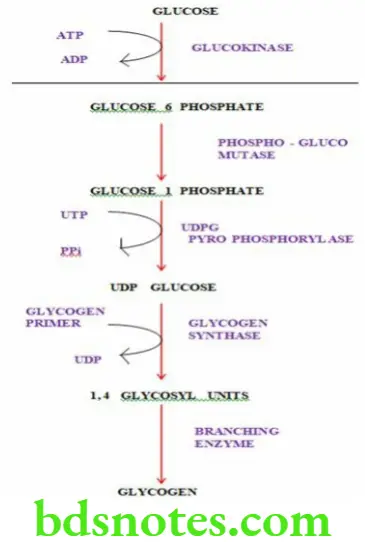
Glycogenesis/Glycogen Synthesis Definition
Glycogenesis is the formation of glycogen from glucose
Glycogenesis/Glycogen Sites
- Glycogenesis takes place in the liver and skeletal muscles
- Storage capacity of glycogen in a normal adult man (70 kg) is
- Liver – 70 to 110 grams
- Skeletal muscles- 240 to 250 grams
Reactions Of Glycogenesis
- Glucose is phosphorylated to glucose 6 phosphate by the enzyme glucokinase
- Glucose 6 phosphate is converted to glucose 1 phosphate by the enzyme phosphoglucomutase
- Glucose 1 phosphate then reacts with UTP (uridine triphosphate) to form UDP glucose (uridine diphosphate glucose) under the influence of the enzyme UDPG pyrophosphorylase
- C1 of the glucose of UDP glucose forms a glycosidic bond with the C4 of glucose of glycogen primer
- The enzyme required is glycogen synthase and UDP is liberated in the reaction
- A pre-existing glycogen primer must be present to initiate the reaction
- In this way an existing glycogen chain can be repeatedly extended by one glucose unit at a time.
- When the chain has lengthened to a minimum of 11 glucose units, branching enzyme transfers 6 glucose units, thus establishing a branch point in the molecule
- The branches grow by further additions and further branching
- 2 ATP’s are required for glycogenesis.
Question 8. HMP Shunt Pathway.
Answer.
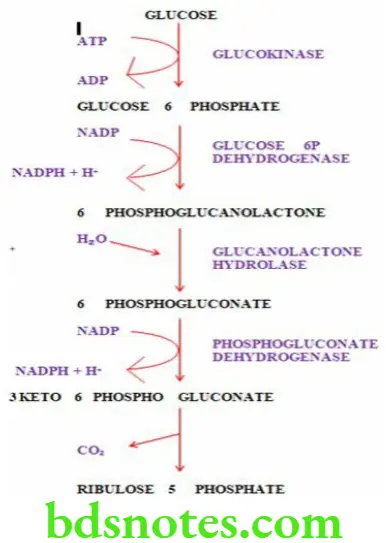
Characteristic Features Of HMP Shunt Pathway
- HMP shunt (hexose mono phosphate shunt) is an alternate pathway for the oxidation of glucose
- HMP shunt is also known as
- Pentose phosphate pathway
- Pentose cycle
- Phospho-gluconate pathway
- Warburg-Dickens-Lipmann pathway
- Direct oxidative pathway
- HMP shunt is a multi cyclic process
- It is not meant to provide energy
- It provides NADPH which is required for various metabolic pathways
- It provides pentoses which are required for nucleic acid synthesis
- Deficiency of the enzyme glucose 6 phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) of the HMP shunt pathway can cause haemolytic anemia
- It occurs in certain specialized tissues e.g. liver, adipose tissue, RBC’s, testes, ovary, adrenal cortex, lactating mammary gland, lens and cornea of the eye
- Carbon dioxide is produced in this pathway
- It takes place in the cytosol
- ATP is required for HMP shunt pathway but ATP is not produced .
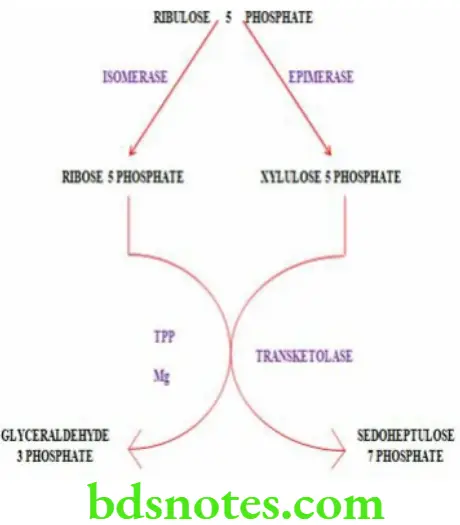
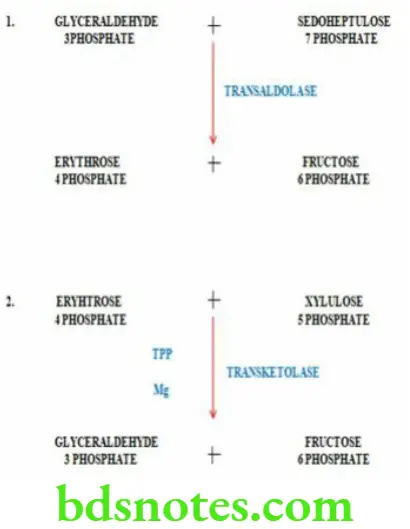
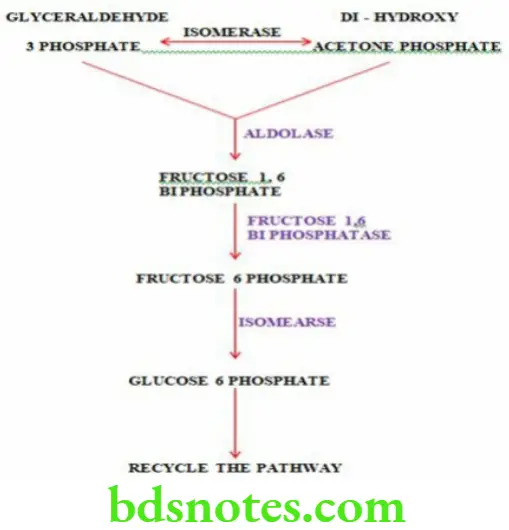
Question 9. Gluconeogenesis.
Answer.
Gluconeogenesis Definition
The formation of glucose from non carbohydrate sources is known as gluconeogenesis
- Gluconeogenesis meets the requirement of glucose in the body when carbohydrates are not available in sufficient amounts in the diet
- Glucose is the only source of energy for nervous tissue and erythrocytes
- Glucose is required to maintain levels of intermediates of the Krebs cycle
- It is a source of glycerol phosphate which is required for the adipose tissue
- It is a precursor of milk sugar lactose for the lactating mammary gland
- Glucose is the only source of energy for skeletal muscles in anaerobic conditions
Sites Of Gluconeogenesis
Gluconeogenesis takes place in the liver and kidneys

Leave a Reply