Bacteriophage
Question 1. Write a short note on bacteriophage.
Answer:
Bacteriophages are viruses that infect and parasitic bacteria. They are also known as phages.
- They may transmit genetic information from one bacterium to another by transduction.
- Bacteriophages that infect E. coli are known as T-even phages and are extremely studied.
- They are present in sewage feces, polluted water, and soil.
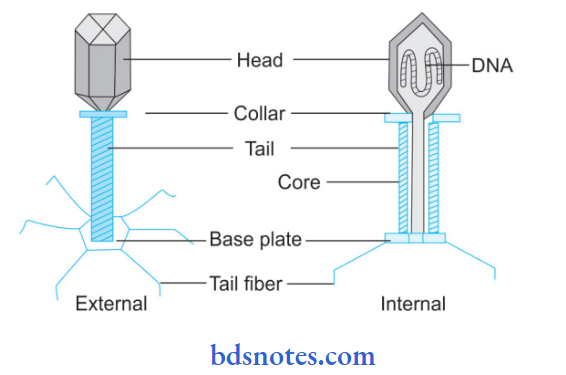
Morphology of Bacteriophage It is formed of the following components, i.e.
- Phage capsid: The phage genome is surrounded by a protein covering called a phage capsid.
- T- even phages are tadpole-shaped and have a head and a tail
- Head: Hexagonal and has double-stranded DNA which is enclosed in a protein coat called a capsid. The size of the head varies in different phages, i.e. 28 to 100 nm.
- Tail: It is cylindrical and is composed of a hollow core surrounded by a contractile sheath and terminal baseplate which has attached to it prongs and tail fibers.
- Genome: Most of the phages consist of a single, linear double-stranded DNA molecule as its genome.
Read And Learn More: Microbiology Question And Answers
Characteristic Of Bacteriophage
- Bacteriophages have high host specificity.
- It can be filtered via filters that hold back bacteria.
- Lytic phages lead to the lysis of bacteria
- They are sensitive to heat and get inactivated by boiling.
- The most common habitat of bacteriophages is the intestinal bacterial flora of man and animal.
Life Cycle of Bacteriophage Depending on its type, on entering the host bacteriophage exhibits two different types of life cycle
- Lytic Cycle: In a virulent or lytic cycle, there is intracellular multiplication of phages producing lysis of infected cells and release of progeny virions.
- Lysogenic Cycle: In a temperate or lysogenic cycle, the phage DNA either becomes integrated with the bacterial genome or exists as a free plasmid in the bacterial cell and replicates synchronously with it, causing no harm to the host cell.
Significance Of Bacteriophage
Phage typing: This is used as an epidemiological marker for establishing the path of transmission of the infectious agent and for identification of the reservoir of infection. Bacteriophages can act as carriers of genes from one bacterium to another, i.e. a process known as transduction. They can confirm the property of toxin production in some of the bacteria.

Leave a Reply