Autonomic Nervous System Cholinergic System And Drugs
Question 1. Explain The Pharmacological Basis For Neostigmine In Myasthenia Gravis.
Answer:
The Pharmacological Basis For Neostigmine In Myasthenia Gravis
Neostigmine is a reversible anticholinesterase. It improves muscle contraction by allowing acetylcholine released from prejunctional.
Endings accumulate and act on receptors over a large area and directly depolarize the endplate in myasthenia gravis.
Question 2. Explain Why Neostigmine Is Preferred Over Physostigmine For Myasthenia Gravis?
Answer:
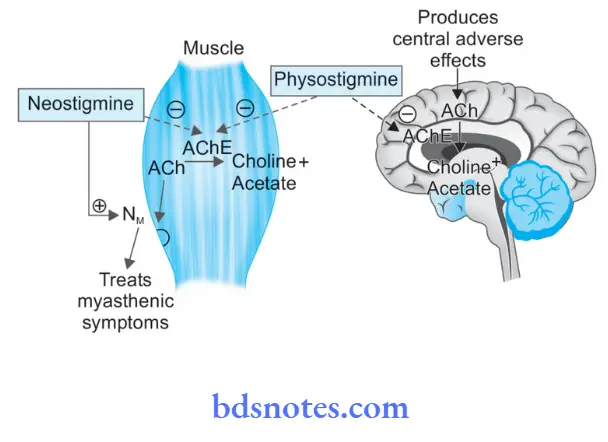
Neostigmine Is Preferred Over Physostigmine For Myasthenia Gravis
Neostigmine is a quaternary ammonium compound and is lipid soluble. Hence it produces its effect only on peripheral tissues.
Neostigmine has direct agonistic action on neuromuscular nicotinic cholinergic (NM) receptors in addition to inhibition of the enzyme cholinesterase.
Read And Learn More: Pharmacology Question And Answers
It does not cross the blood-brain barrier and produces no central side effects.
On the other hand, physostigmine has a less nicotinic effect at the neuromuscular junction, it also crosses the blood-brain barrier and produces central side effects.
Physostigmine has direct agonistic action on nicotinic cholinergic receptors.
That’s why neostigmine is preferred over physostigmine in myasthenia gravis.
Question 3. Write Briefl On Physostigmine.
Answer:
Physostigmine
Physostigmine is a reversible anti-cholinesterase. Physostigmine is a naturally occurring lipid-soluble tertiary amine.
Due to lipid solubility physostigmine can be given orally and it can cross the blood-brain barrier and corneal membrane efficiently.
Physostigmine Mechanism Of Action
Reversible anticholinesterase is an agent which inhibits true and pseudocholinesterase and protects acetylcholine from hydrolysis.
In this way, acetylcholine gets accumulated and hence potentiates the cholinergic effect.
Physostigmine Uses
- Glaucoma: Physostigmine decreases intraocular pressure by causing miosis and facilitates the draining of aqueous humor.
- Physostigmine is also given to reduce adhesion formation between the iris and lens or the iris and cornea.
- In belladonna poisoning: Physostigmine is given because it reverses both the central and peripheral effects of atropine poisoning. Physostigmine acts as a specific antidote.
Adverse Effects Of Physostigmine
Miosis, hypotension, cardiac arrhythmias, lacrimation, salivation, sweating, tracheobronchial secretion, abdominal cramps, respiratory depression, convulsion, comma, and finally death.
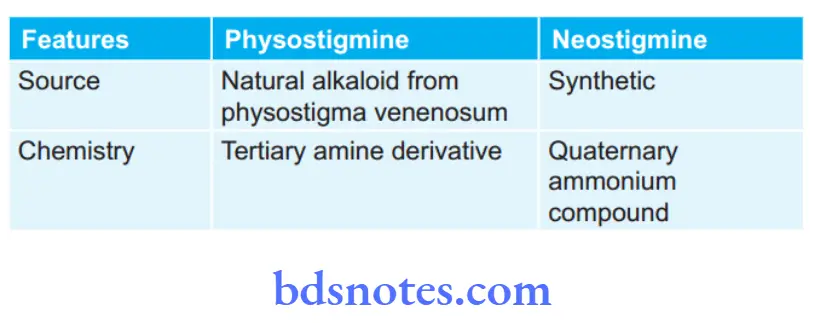
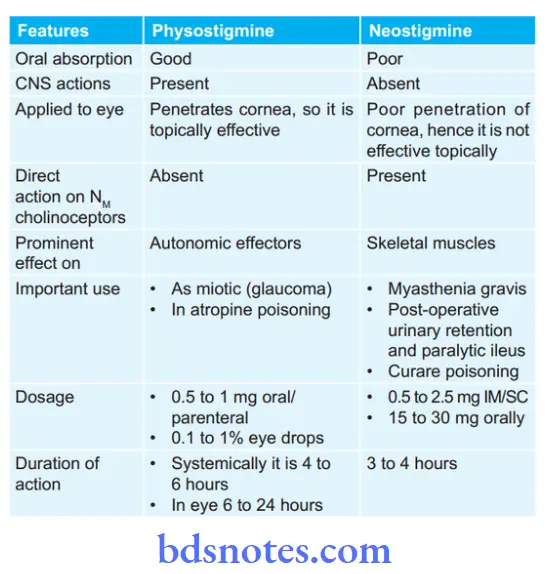
Question 4. Write the Difference Between Neostimine And Physostigmine.
Answer:
Difference Between Neostimine And Physostigmine

Leave a Reply