Arm
Question 1. Enumerate the muscles on the front of arm and give their nerve supply.
Answer.
The muscles on the front of arm are
- Biceps brachii
- Coracobrachialis
- Brachialis
All these muscles are supplied by the musculocutaneous nerve.
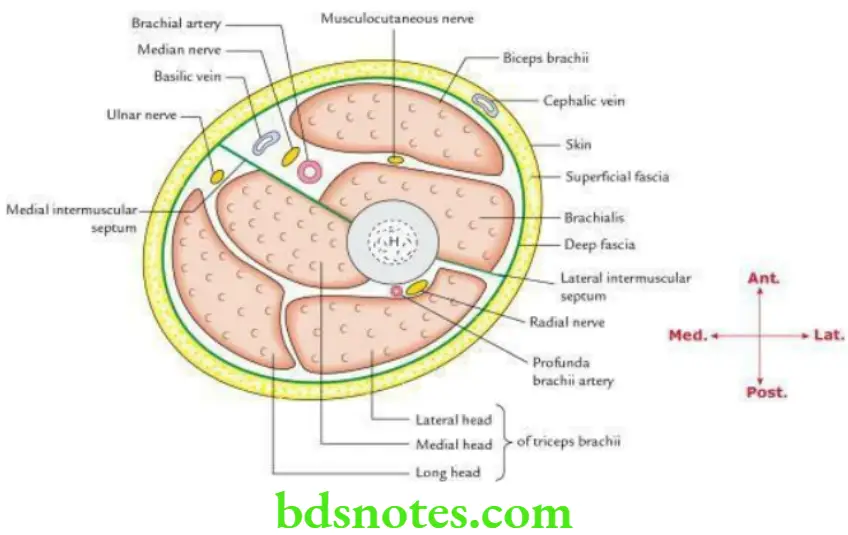
Question 2. Draw the transverse section of arm at the level of insertion of coracobrachialis to show the arrangement of various structures.
Answer.
The transverse section of arm.
Question 3. Give the origin, insertion, nerve supply and actions of biceps brachii.
Answer.
Origin
Biceps brachii arises by two heads:
- Long head arises from the supraglenoid tubercle of scapula (origin is intracapsular but extrasynovial).
- Short head arises from the tip of coracoid process of scapula along with coracobrachialis.
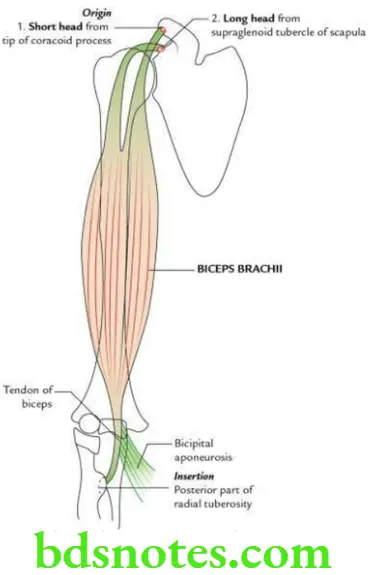
Insertion
By a tendon into the tuberosity of radius (posterior rough part).
Nerve supply
Musculocutaneous nerve.
Actions
- Flexor of elbow joint.
- Supinator of forearm when elbow is flexed.
- Long head keeps the head of humerus in position during abduction of shoulder joint.
Question 4. Name the joints at which biceps brachii acts and tell the movements that it produces at these joints.
Answer.
- Biceps brachii acts at three joints: (a) shoulder joint, (b) elbow joint and (c) superior radioulnar joint.
- Movements produced at these joints are
- At shoulder joint: Flexion of arm (by short head)
- At elbow joint: Flexion of forearm
- At superior radioulnar joint: Supination of forearm when forearm is semiflexed in midprone position
Read And Learn More: Selective Anatomy Notes And Question And Answers
Question 5. Give the origin, insertion, nerve supply and actions of coracobrachialis.
Answer.
Origin
From the tip of coracoid process of scapula along with the short head of biceps brachii.
Insertion
In the middle of the medial border of the shaft of humerus.
Nerve supply
Musculocutaneous nerve.
Actions
Adducts the arm and flexes the shoulder joint.
Question 6. Give the origin, insertion, nerve supply and actions of brachialis.
Answer.
Origin
From lower half of the front of humerus and medial and lateral intermuscular septa.
Insertion
Into coronoid process and tuberosity of ulna.
Nerve supply
- Musculocutaneous nerve
- Radial nerve (supplies only a small lateral part)
Action
Flexor of elbow joint.
Question 7. Describe the musculocutaneous nerve in brief.
Answer.
The musculocutaneous nerve, as its name implies, supplies the muscles of front of arm and skin on the lateral side of forearm.
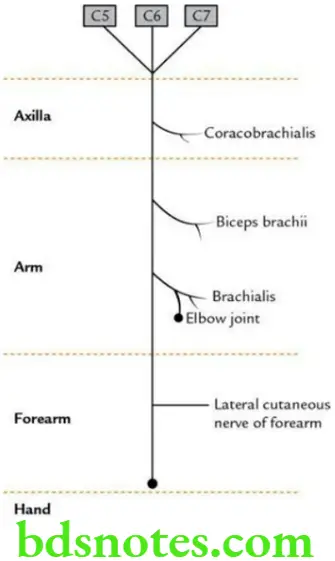
Origin
From lateral cord of brachial plexus (C5, C6 and C7).
Course
It arises obliquely from the lateral cord of brachial plexus behind pectoralis minor muscle. There it lies lateral to axillary artery. It pierces coracobrachialis muscle and reaches the lateral side of the arm. Then it runs laterally downwards between biceps brachii and brachialis muscles. At the crease of elbow, it pierces the deep fascia lateral to the tendon of biceps brachii from where it continues as lateral cutaneous nerve of forearm.
Branches
Muscular:
To coracobrachialis, biceps brachii and brachialis.
Cutaneous:
Lateral cutaneous nerve of forearm to lateral side of forearm.
Articular:
To elbow joint.
Applied anatomy
Isolated lesions of the musculocutaneous nerve are rare.
Question 8. Describe the brachial artery in brief and discuss its applied anatomy.
Answer.
Origin
The brachial artery is continuation of the axillary artery below the lower border of teres major muscle.
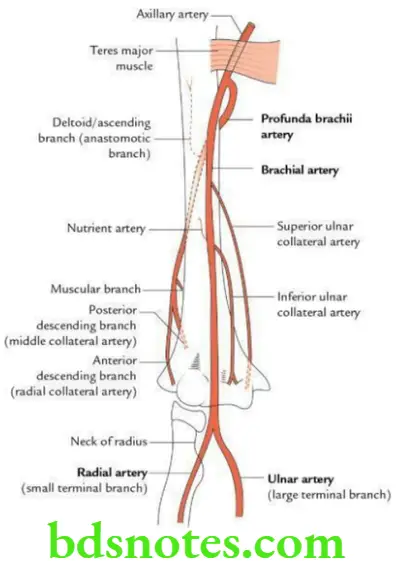
Course
It runs downward to reach the cubital fossa where it terminates at the level of neck of radius by dividing into radial and ulnar arteries.
Branches
Apart from the muscular branches, the named branches of brachial artery are
- Profunda brachii artery (largest branch)
- Nutrient artery to humerus
- Superior and inferior ulnar collateral arteries
Applied anatomy
- Blood pressure is recorded by auscultating the pulsations of brachial artery in the cubital fossa medial to tendon of biceps brachii.
- Brachial artery can be compressed digitally at midarm against the tendon of coracobrachialis on the medial side of the humerus.
- Brachial artery may be ruptured in supracondylar fracture of humerus.
Question 9. Write a short note on profunda brachii artery.
Answer.
Origin
It is the largest (main) branch of brachial artery arising just below the lower border of teres major muscle.
Course
The artery accompanies the radial nerve posteriorly in the radial groove, deep to triceps. In radial groove, it gives various branches.
Branches
Apart from muscular branches, the name of branches of profunda brachii artery are:
- Nutrient artery to humerus near the deltoid tuberosity.
- Ascending branch, ascends between long and lateral heads of triceps to anastomose with posterior circumflex humeral artery.
- Radial collateral artery is the continuation of the profunda brachii artery and pierces the lateral intermuscular septum with the radial nerve, reaches the elbow and anastomoses with the radial recurrent artery.
- Middle collateral artery, also called posterior descending branch, descends through the medial head of triceps, reaches the elbow and anastomoses with the interosseus recurrent artery.
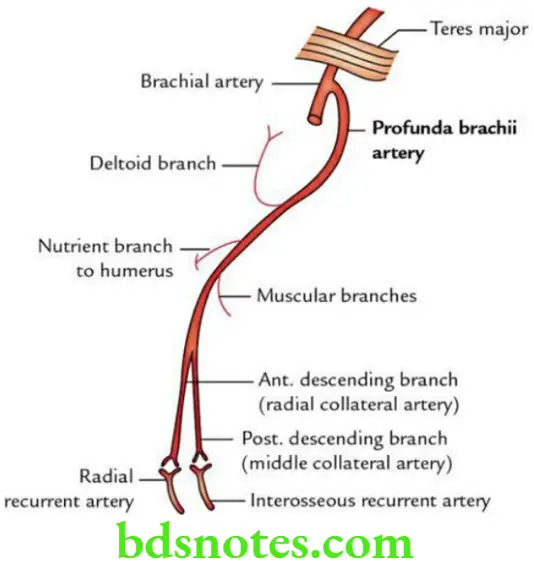
Applied anatomy
Branches of profunda brachii artery take part in the formation of arterial anastomosis around elbow.
Question 10. Enumerate the various anatomical events that occur at the level of insertion of coracobrachialis.
Answer.
The anatomical events occurring at the level of insertion of coracobrachialis are:
- Circular shaft of humerus becomes triangular below this level.
- Deltoid and coracobrachialis are inserted at this level.
- Upper end of origin of brachialis extends up to this level.
- Brachial artery passes from medial side of arm to its anterior aspect.
- Basilic vein pierces the deep fascia at this level.
- Median nerve crosses in front of brachial artery from lateral to medial side.
- Radial nerve pierces lateral intermuscular septum to pass from the posterior compartment of arm to the anterior compartment of arm.
- Ulnar nerve pierces medial intermuscular septum to go from the anterior compartment of arm to the posterior compartment of arm.
- Medial cutaneous nerves of arm and forearm pierce the deep fascia at this level.
- Nutrient artery pierces the humerus at this level.
Therefore, the site of insertion of coracobrachialis is an important anatomical landmark in the arm.
Question 11. Enumerate the contents of posterior compartment of the arm.
Answer.
The contents of posterior compartment of arm are:
- Triceps brachii muscle
- Radial nerve
- Profunda brachii artery
Question 12. Give the origin, insertion, nerve supply and actions of triceps brachii.
Answer.
Origin
Triceps brachii muscle arises by three heads – long, lateral and medial.
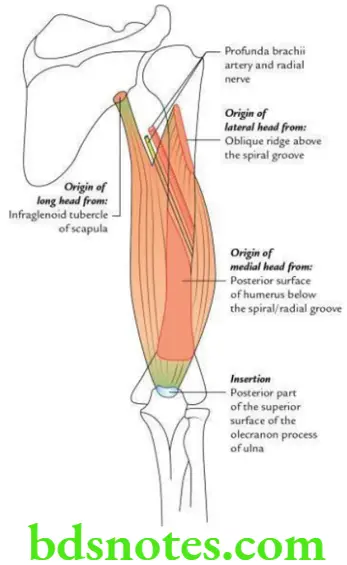
Long head:
From infraglenoid tubercle of scapula.
Lateral head:
From oblique ridge above the spiral groove (i.e. lateral lip of the spiral groove).
Medial head:
From posterior surface of shaft of humerus below the level of spiral groove.
Insertion
Into the posterior part of the superior surface of olecranon process of ulna.
Nerve supply
Radial nerve (C7, C8).
Note. Each head is supplied by a separate branch. The branch supplying long head arises in axilla, the branch supplying lateral head arises in spiral groove and the branch supplying medial head arises both in axilla and spiral groove.
Action
Extensor of elbow.
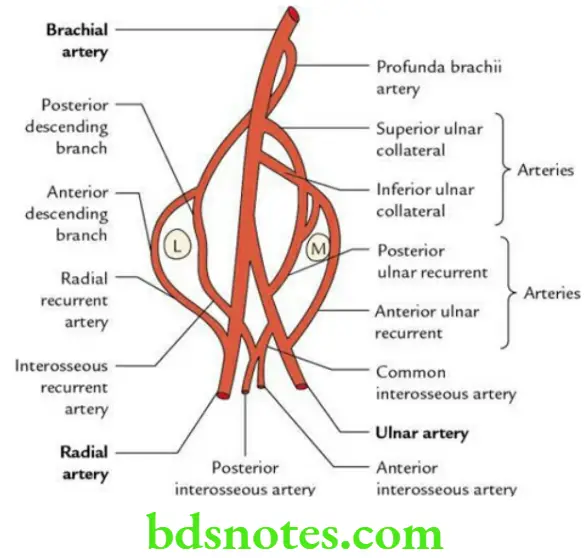
Question 13. Write a short note on the arterial anastomosis around the elbow joint.
Answer.
The arterial anastomosis around the elbow joint is formed between the branches of the following arteries:
- Brachial artery
- Radial artery
- Ulnar artery
Question 14. Write a short note on cubital fossa.
Answer.
Cubital fossa is a triangular hollow in front of the elbow joint.
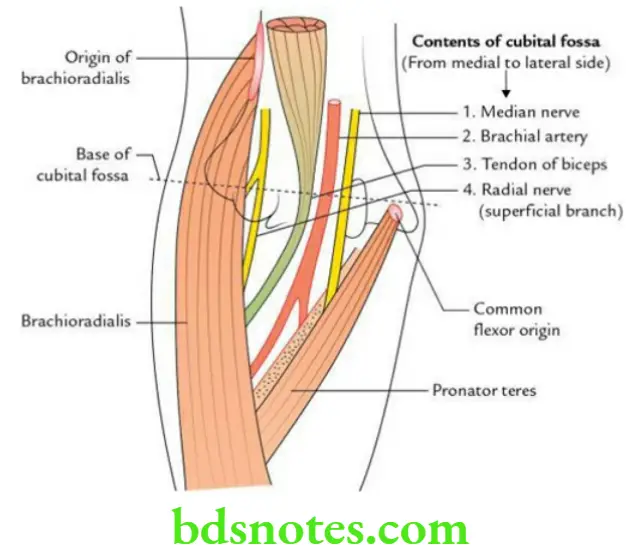
Boundaries
- Base is formed by an imaginary horizontal line, joining the medial and lateral epicondyles of the humerus.
- Medial wall is formed by pronator teres.
- Lateral wall is formed by brachioradialis.
- Roof is formed by skin, superficial fascia, deep fascia, and bicipital aponeurosis.
- The superficial fascia contains median cubital vein, lateral cutaneous nerve of forearm and medial cutaneous nerve of forearm.
- Floor is formed by brachialis muscle in the upper and medial part, and supinator muscle in the lower and lateral part.
- Apex is a point where pronator teres disappears underneath the brachioradialis muscle.
Contents
From medial to lateral side:
- Median nerve
- Brachial artery
- Biceps tendon
- Superficial branch of radial nerve
Mnemonic: MBBS.
Applied anatomy
- The brachial artery is auscultated in cubital fossa for recording the blood pressure.
- The median cubital vein is used in the region of cubital fossa for venipuncture, as it lies superficial to bicipital aponeurosis and is the most fixed vein.

Leave a Reply