Antiparkinsonian Drugs
Question 1. Give A Brief Account Of Levodopa.
Levodopa is a dopamine precursor.
Account On Levodopa Mechanism of Action
- Levodopa crosses the blood-brain barrier and is taken up by presynaptic terminals of dopaminergic neurons and is dehydroxylated to dopamine.
- Levodopa is converted to dopamine in peripheral tissue and dopamine thus formed acts on the heart, blood vessels, and peripheral organs.
Read And Learn More: Pharmacology Question And Answers
Account Of Levodopa Pharmacological Actions
- CNS: Hypokinesia, rigidity, and tremors improve first, later other symptoms like gait, speech, sialorrhea, and mood are normalized.
- CVS: It causes tachycardia
- CTZ: It causes nausea and vomiting.
- Endocrine: It inhibits prolactin release.
Account Of Levodopa Adverse Reaction
- GIT: It causes nausea, vomiting, and anorexia in early treatment. Tolerance to emetic effect develops slowly.
- CVS: It causes postural hypotension, palpitation, cardiac arrhythmia, and angina.
- Abnormal movement: Dyskinesia, tics, tremors, and choreoathetosis movements may occur.
- Behavioral effect: Agitation, anxiety, nightmares, depression, confusion, and mania.
Question 2. Explain Why Levodopa Is Given Along With Carbidopa?
Or
Write A Short Note On Levodopa And Carbidopa Combination.
Answer:
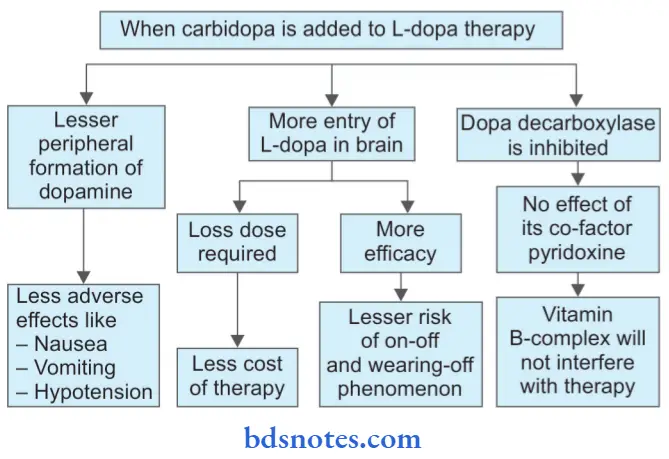
Decarboxylase inhibitor, i.e. carbidopa prevents the conversion of levodopa to dopamine outside the brain by inhibiting dopa decarboxylase enzyme peripherally. Thus, a greater concentration of levodopa can cross the blood-brain barrier and reaches its site of action in the brain.
Benefits obtained from combining levodopa with carbs-dopa are:
- The combination ensures less degree of peripheral decarboxylation of levodopa and thus more entry into the brain. This improves the efficacy of levodopa
- The greater amount of levodopa also contributes to the possibility of a reduction in the dose of the drug administered.
- Reduced conversion of levodopa and less formation of dopamine in the periphery leads to a reduction in the incidence of adverse effects like nausea, vomiting, cardiac complications, etc. with levodopa.
- Reduced cost of total therapy to the patient because of lesser amount of drugs required to maintain their clinical efficacy.
- Sustained levels of dopamine attained in the CNS ensure minimal incidence of ”on-off phenomenon.
- Reduction in drug interactions especially with drugs acting on the dopa decarboxylase enzyme like pyridoxine.

Leave a Reply