Antimicrobial sensitivity testing
Question 1. Write a short note on the antibiotic sensitivity test.
Or
Write a short note on antibiotic sensitivity testing.
Answer:
Antibiotic sensitivity testing is also known as antimicrobial susceptibility testing.
This is performed in vitro to determine:
- Susceptibility of given microorganism to know the concentration of drug
- Potency of antibiotic
- The concentration of antibiotics in body fluid and tissues.
Types of Sensitive Testing
Antibiotic sensitivity tests are of two types, i.e.
- Diffusion test:
- Disc diffusion method
- Cup method
- Cylinder method
- Dilution test:
- Broth dilution method
- Agar dilution method
Read And Learn More: Microbiology Questions and Answers
1. Diffusion Tests:
These tests are used widely and determine the susceptibility of clinical isolates to antibiotic agents that are to be used in the treatment. The principle of these tests is to allow antibiotic agents to be diffused through a solid medium, so the concentration of antibiotic is highest near the site of application of antibiotic agent and decreases with distance. Diffusion tests are of three types, i.e. disc diffusion method, cup method, and cylinder method. Out of all these, disc diffusion methods are commonly used.
- Disc Diffusion Method:
- The principle of this method is the addition of a known amount of an antimicrobial agent to a fitter paper disc which measures 6 mm in diameter.
- Placing of this disc over the surface of agar which is previously inoculated with a bacterium should be tested, this will result in the development of a zone of inhibition of growth around the disc.
- Disc diffusion methods are of three types, i.e. Kirby–Bauer disc diffusion method, Stokes disc diffusion method, and Epsilometer test.
- Kirby-Bauer Disc Diffusion Method:
- This is the most commonly used method.
- This method is used to determine the susceptibility of clinical isolates to antimicrobial agents.
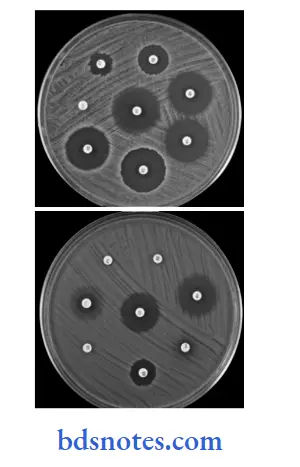
- Procedure Diffusion Method:
- In this procedure two discs are used, i.e. one is the control disc and another is the test disc.
- Inoculate the standardized inoculums with a sterile cotton swab on the surface of the agar plate and allow the plate to get dry for 3 to 5 minutes.
- Apply a disc of antibiotic agents to the surface of agar plates by a mechanical dispenser or by hand using sterile forceps. Place the discs family.
- On the plate of 100 mm, seven discs are placed, i.e. one in the center and six on the periphery.
- Control strains of S. aureus, E. coli, P. aeruginosa, etc. should be tested every time.
- Keep the plates in a refrigerator at 4°C for 30 minutes for diffusion, and then incubate at 37°C for 16 to 18 hours.
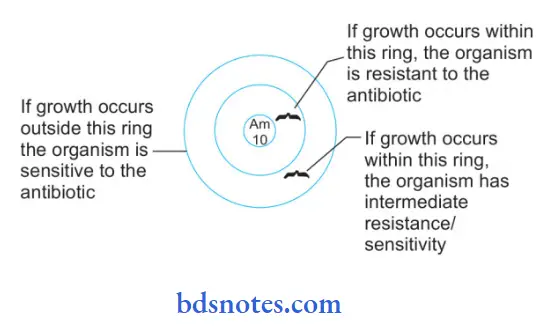
- Result Diffusion Method: The diameter of the zone of growth inhibition around each disc should be measured by calipers, or else by viewing the plate against a ruler or ruling the screen. Zones should be compared by zones of inhibition of standard control strain. Interpretation of results should be:
- Sensitive: If the zone diameter of the test organism is greater than, equal to, or not more than 4 mm less than that of the control strain.
- Intermediate sensitive: If the zone diameter is at least 12 mm but decreases by more than 4 mm as compared to the control strain.
- Resistant: When the diameter shows no zone of inhibition of growth or if the zone diameter is not more than 10 mm
It is similar to the Kirby-Bauer disc diffusion method, but the difference is that in the Stokes disc diffusion method, the control culture and test culture are grown on the same plate for comparing zones of inhibition produced in two cultures by the same disc.
Stokes Disc Diffusion Method
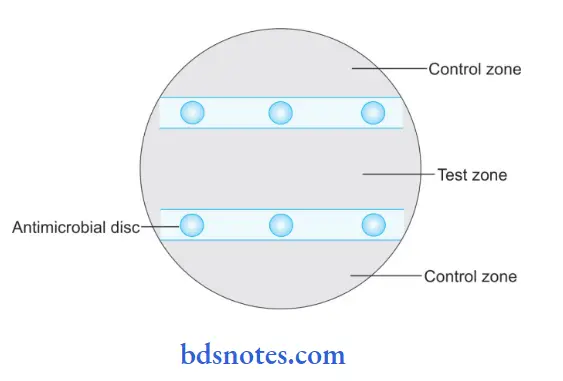
- Procedure Of Stokes Disc Diffusion Method:
- Inoculate the test bacterium over the middle third of the culture plate and control culture over the upper and lower third of the plate carefully by leaving an uninoculated strip of 5 mm between the test and control areas, these are used for placing discs.
- As inoculation is over, place the discs, three on each side, between the control and test inocula.
- Refrigerate the plates for diffusion and incubate them at 37°C for 16 to 18 hours.
- Result Of Stokes Disc Diffusion Method: Interpretation of results is carried out by measuring and comparing zones of inhibition of control and test bacterium, as:
- Sensitive: If the zone of inhibition of the test organism is greater or equal to or not less than 3 mm than that of the control strain.
- Intermediate sensitive: If the zone diameter of the test bacterium is at least 2 mm and the difference between a zone of the test and control strain is 3 mm.
- Resistant: If the zone diameter of the test bacterium is less than 2 mm.
Epsilometer Test (E Test)
E test is the modification of the agar diffusion sensitivity test and detects the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of an antibiotic.

- Procedure Of Epsilometer Test (E Test):
- Inoculate the test bacterium and an absorbent strip with a known gradient of antibiotic concentration along with its length is placed on agar.
- Keep the plates in the refrigerator for diffusion and then incubate at 37°C for 16 to 18 hours.
- Antibiotic undergoes diffusion in the medium and inhibits growth.
- Result Of Epsilometer Test (E Test): A low concentration of the gradient which inhibits the growth of the organism is considered as detecting minimum inhibitory concentration.
2. Dilution test
Broth Dilution Method: This method regulates therapeutic dose accurately. It demonstrates a small degree of resistance This method is also used to study the antimicrobial sensitivity of slow-growing bacteria, for example, Tubercle bacilli.
- Procedure Of Dilution test:
- A graded amount of antibiotic agent is incorporated in
- Mueller–Hinton broth in a test tube.
- Inoculate the media with the test bacterium.
- Control strain with known sensitivity is inoculated in a separate set.
- Carry out incubation at 37°C for 16 to 18 hours.
- Result Of Dilution test:
- The endpoint should be taken as minimum inhibitory concentration or minimum bactericidal concentration (MBC).
- MIC is the amount of antimicrobial agent needed to inhibit the growth.
- MBC is the amount of antimicrobial agent needed to kill the bacteria.
- Detection of MIC is done by noting the lowest concentration of antimicrobial agent which shows no visible growth.
- Detection of MBC is done by taking subculture from each tube which shows no growth on a suitable medium without any antimicrobial agent.
- A loopful from each tube is inoculated over different plates and is incubated at 37°C for 16 to 18 hours and a tube containing the lowest concentration of antimicrobial agent that fails to show growth on subculture is considered as MBC.
Agar Dilution test: This method is used to study the antimicrobial sensitivity of a large number of isolates at a single time. It determines the MICs of a large number of isolates.
- Procedure Of Agar Dilution Test:
- Prepare the serial dilutions of antimicrobial agents.
- Add 1.5 mL of each dilution to 13.5 mL of melted agar suspension and pour in plates.
- In this manner, plates with different concentrations should be prepared.
- Inoculate many strains over each plate. Inoculate each strain under test on an agar plate which consists of different known concentrations of the same antimicrobial agent.
- A control plate devoid of antimicrobial agents should be inoculated.
- Incubate the plates at 37°C for 16 to 20 hours.
- As incubation gets over results should be recorded.
- Result Of Agar Dilution test: The lowest concentration of antimicrobial agent which allows not more than one or two colony-forming units or only a slight haze to grow is taken as minimum inhibitory concentration

Leave a Reply