Question 11. Write a short note on ameloblastoma.
Answer:
Ameloblastoma is defined as “usually unicentric, nonfunctional, intermittent in growth, anatomically benign and clinically persistent”. Robinson
Pathogenesis of Ameloblastoma
The tumor may derive from the:
- Cell rest of enamel organ, either remnants of the dental lamina or remnants of Hertwig’s sheath, the epithelial rest cells of Malassez
- Epithelium of odontogenic cyst, i.e. dentigerous cyst or odontomas
- Disturbance of the developing enamel organ
- The basal cell of the surface epithelium of the jaw
- Heterotrophic epithelium in other parts of the body especially in the pituitary gland.
Ameloblastoma Clinical Features
- Ameloblastoma occurs in2nd, 3rd, 4thand 5thdecade of life
- The mean age of occurrence is 32 years
- Males are affected more commonly than females.
- Ameloblastoma in most cases involves the mandible in the molar ramus area
- Clinically ameloblastoma presents slow enlarging, painless, ovoid, and fusiform bony hard swelling of the jaw
- Pain, paresthesia, and mobility of regional teeth are present in some cases
- Pathological fractures may occur in many affected bones.
Ameloblastoma Gross Appearance
Grossly the tumor is grayish white, usually solid, sometimes cystic, replacing and expanding the affected bone.
Ameloblastoma Histopathology
Histologically the ameloblastoma shows neoplastic proliferation of odontogenic epithelial cells mostly in four distinct patterns.
- Follicular type
- Plexiform type
- Acanthomatous type
- Granular type.
Follicular Type:
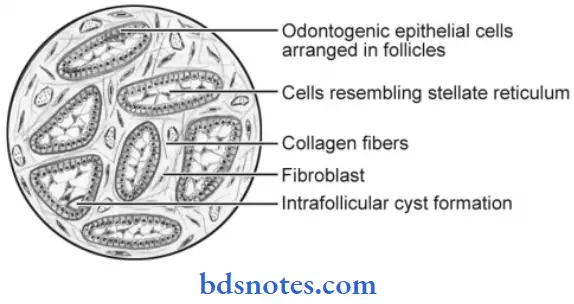
- The neoplastic odontogenic epithelial cells proliferate in the form of multiple discrete follicles and islands within fibrous connective tissue stroma.
- Each follicle-like structure is bordered on the periphery by a single layer of tall columnar cells resembling ameloblasts.
- The cells located at the center of the follicle are loosely arranged and resemble stellate reticulum cells. Microcyst formation is often observed inside these follicles.
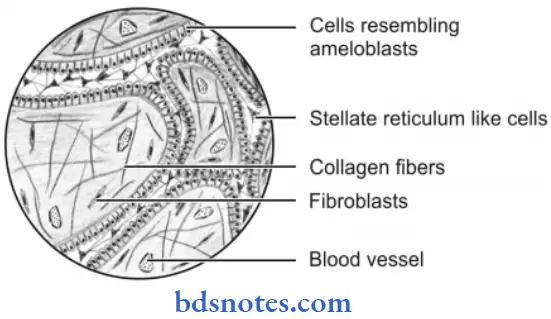
Plexiform Type
- This pattern of neoplastic cell proliferation is also often called a fish net-like pattern.
- The peripheral layer of cells is tall and columnar in nature and often resembles ameloblastoma.
- Cells situated at the center portion of strands resemble the stellate reticulum.
- The intervening connective tissue stroma is thin with minimum cellularity and shows multiple areas of cystifiation which may be either large or small in number.
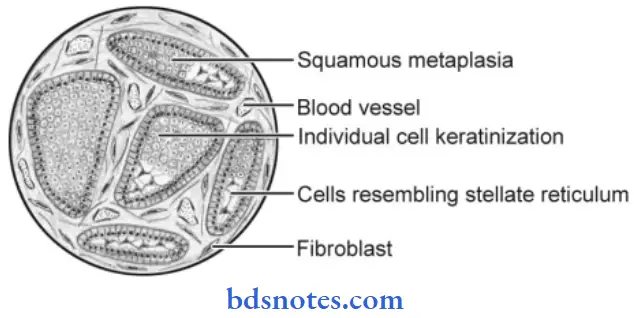
Acanthomatous Type
- The cells occupying the position of the stellate reticulum undergo squamous metaplasia, sometimes with keratin formation in the anterior portion of tumor islands.
- Occasionally, epithelial or keratin pearls may be observed
- Areas of calcification may be found in the metaplastic squamous epithelium.
- It may be confused with the squamous cell carcinoma.
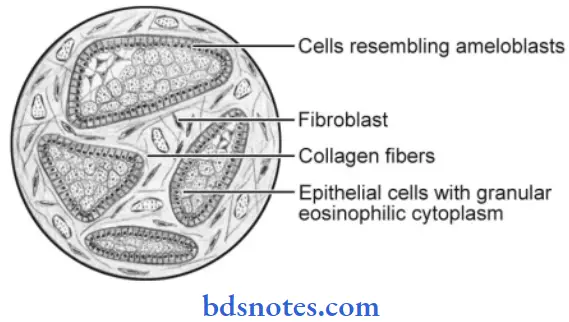
Granular Type
- There is a marked transformation of the cytoplasm, usually of the stellate reticulum-like cells that it takes a very coarse granular eosinophilic appearance.

Leave a Reply