AIDS And The Periodontium
Question 1. Write in brief on AIDS and periodontium.
Or
Write short note on AIDS and periodontium.
Answer. Most of opportunistic infections are seen in AIDS patients caused by protozoan, fungal or viral pathogens. The most destructive and problematic are those of bacterial origin. The bacterial infection seen in HIV positive patients includes disease caused by encapsulated bacteria, i.e. Campylobacter, Klebsiella, Salmonella and Streptococcus.
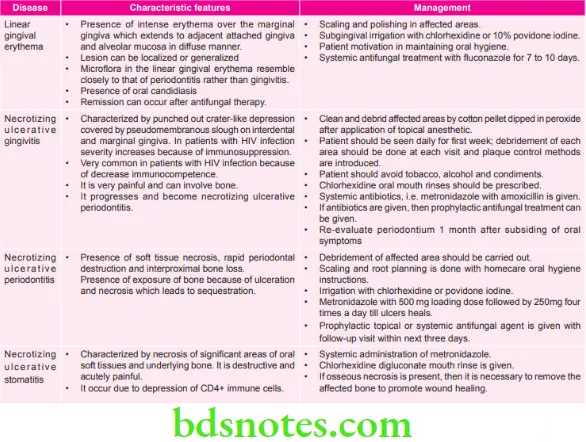
Classification of Periodontal Disease Associated with HIV Infection
- Linear gingival erythema
- Necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis
- Necrotizing ulcerative periodontitis
- Necrotizing ulcerative stomatitis
Read And Learn More: Periodontics Question And Answers
Description of Periodontal Disease Associated with Aids
Question 2. Write short note on AIDS.
Answer. Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) is a severe immune deficiency which is characterized by profound impairment of the immune system arising from infection with HIV. It is accompanied by one of the following symptoms:
- Life-threatening opportunistic infection
- Persistent fever
- Unusual cancers
- Chronically swollen lymph nodes
- Weight loss and diarrhea
- Neurological disorders
Staging of AIDS Patients
As per the CDC surveillance case classification (1993) AIDS patients are grouped as:
- Category 1: More than or equal to 500 CD4 lymphocytes/mm3
- Category 2: 200 to 499 CD4 lymphocytes/mm3
- Category 3: Less than 200 CD4 lymphocytes/mm3.
Management Of AIDS
Current recommendation for treatment of HIV-infected patients include high active antiretroviral therapy (HAART), which consists of three or more drugs:
- Nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors, e.g. Azidothymidine, Stavudine, Lamivudine and others
- Non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors e.g. Viramune, nevirapine
- Protease inhibitors: Ritonavir, Indinavir.
In HAART, regime include atleast one protease inhibitor or non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor. As HAART is also known as drug cocktail or triple therapy.
Question 3. Write short note on atypical ulcers.
Answer. Atypical ulcers are also known as non-healing ulcers.
- Atypical ulcers are found to be co-infected with HSV (Herpes simplex virus) and CMV (cytomegalovirus) or with EBV (Epstein-Barr Virus).
- These ulcers are more common in individuals who are neutropenic in conjunction with their HIV infection.
- Atypical ulcers are more severe and persistent in individuals with low CD4 cell counts.
- Atypical ulcers may require biopsy, microbial cultures or both to determine the etiology

Leave a Reply