Adverse Drug Effects
Question 1. Give Description Of DrugInduced, Disease.
Answer:
DrugInduced Disease
Drug-induced diseases are also called iatrogenic diseases or physician-induced diseases.
These are functional diseases caused by drugs that persist even after the offending drug has been withdrawn and largely eliminated.
Examples,
- Peptic ulcer by salicylates and corticosteroids.
- Parkinsonism by phenothiazines and other antipsychotics.
- Hepatitis by isoniazid.
- Discoid lupus erythematosus by hydralazine.
Read And Learn More: Pharmacology Question And Answers
Question 2. Define And Differentiate Side Effcts From Adverse Drug Effects. Describe The Adverse Reaction Of The Drug In Detail Giving Suitable Examples.
Answer:
Differentiate Side Effcts From Adverse Drug Effects
The term adverse drug reaction has been defined as any noxious effect which is suspected to be due to a drug occurring at doses normally used.
Require treatment or decrease in dose or indicates caution in the future use of the same drug.
The Adverse Effect Of Drugs Has Been Classified As:
1. Predictable Reaction
These are related to the pharmacological effect of a drug. They include:
- Side Effects: These are unwanted but often unavoidable pharmacodynamic effect that occurs at therapeutic doses.
- A side effect may be based on the same action of the drug, for example, dryness of the mouth with atropine.
- A side effect may be based on a different facet of action, for example, estrogen causes nausea.
- Aneffctmay be therapeutic in one contact but side effects in another contact, for example, codeine used for cough, produces constipation as a side effect.
- Secondary Effect: These are indirect consequences of a primary action of a drug, for example, suppressing bacterial flora by tetracyclines can result in superinfection.
- Toxic Effects: These effects are resulted due to overdosage or prolonged use of drugs, for example, coma by barbiturates, and complete AV block by digoxin.
- Drug Habituation And Dependence: Drugs capable of altering moods and feelings are liable to repetitive use to derive a feeling of euphoria to escape from reality, social adjustment, etc.
- Drug Withdrawal Reaction: Sudden withdrawal or stoppage of certain drugs can result in a type of adverse reaction.
For example, withdrawal of beta blockers can precipitate an effect of myocardial infarction.
Withdrawal of phenytoin can precipitate status epilepticus. - Teratogenic Effect: This refers to the ability of the drug to cause congenital abnormality in the fetus when given during pregnancy, Example. cleft palate following the use of corticosteroids.
- Drug-Induced Disease Or Iatrogenic Diseases: When certain drugs are used chronologically, they can produce disease, for Example. chronic use of aspirin can lead to the production of peptic ulcers.
2. Unpredictable Reactions
These are based on the peculiarities of the patient and not on the drug action.
- Drug allergy: It is an immunologically mediated reaction producing stereotype symptoms that are unrelated to the effect of the drug or its doses.
For Example. anaphylactic reactions resulting in urticaria§§, etching, angioedema, and asthma. - Photosensitivity: It is a cutaneous reaction, resulting from drug-induced sensitization of the skin to UV radiation. Drugs that cause such reactions are demeclocycline and chloroquine.
- Idiosyncrasy: It is generally determined as abnormal reactivity to a chemical. Certain
adverse effects of some drugs are restricted to individuals with a particular genotype.
For Example. barbiturates cause excitement and mental
confusion in some people.
Question 3. Write A Note On Teratogenicity.
Or
Write A Short Note On Teratogenicity.
Or
Give Description Of Teratogenic Drugs.
Answer:
Teratogenic Drugs
It refers to the capacity of a drug to cause fetal abnormalities when administered to the pregnant mother.
- The placenta does not strictly constitute a barrier and any drug can cross it to a greater or lesser extent.
- The embryo is one of the most dynamic biological systems and in contrast to adults, drug effects are often irreversible.
Drugs Can Affect The Fetus In 3 Stages
- Fertilization And Implantation: Conception to 17 days failure of pregnancy which often goes unnoticed.
- Organogenesis: l8 to 55 days of gestation—the most vulnerable period, deformities are produced.
- Growth And Development: 56 days onwards-developmental and functional abnormalities can occur, for Example. ACE inhibitors can cause hypoplasia of organs, especially lungs, and kidneys; NSAIDs may induce premature closure of
ductus arteriosus.- The type of malformation depends on the drug as well as the stage of exposure to the teratogen.
- Fetal exposure depends on the blood level and duration for which the drug remains in maternal circulation.
- The teratogenic potential of a drug is to be considered against the background of congenital abnormalities occurring spontaneously
- It is, therefore, wise to avoid all drugs during pregnancy unless compelling reasons exist for their use regardless of the assigned pregnancy category or presumed safety.
Certain Examples Of Teratogenic Drugs
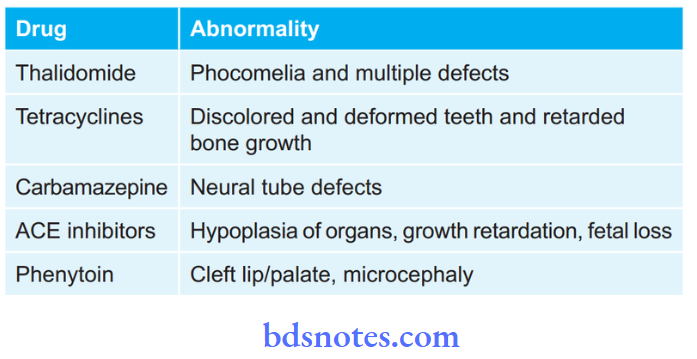
Question 4. Write In Short About Type A Adverse Reactions.
Answer:
Type A Adverse Reactions
It is known as a predictable reaction or augmented reaction.
These are based on the pharmacological properties of the drug which means that they are augmented but qualitatively normal responses to the drug.
Include side effects, toxic effects, and consequences of drug withdrawal.
They are more commonly dose-related and mostly preventable and reversible. They include:
- Side effects: These are unwanted but often unavoidable pharmacodynamic effects that occur at therapeutic doses:
- A side effect may be based on the same action of the drug, for example, dryness of the mouth with atropine.
- A side effect may be based on a different facet of action, for example, estrogen causes nausea.
- An effect may be therapeutic in one context but a side effect in another context, for example, codeine used for cough, produces constipation as
a side effect.
- Secondary effect: These are indirect consequences of a primary action of a drug, for Example. suppressing bacterial flora by tetracyclines can result in superinfection.
- Toxic effects: These effects result due to overdosage or prolonged use of drugs, for example, coma by barbiturates, and complete AV block by digoxin.
- Drug habituation and dependence: Drugs capable of altering moods and feelings are liable to repetitive use to derive a feeling of euphoria to escape from reality, social adjustment, etc.
- Drug withdrawal reaction: Sudden withdrawal or stoppage of certain drugs can result in a type of adverse reaction.
- For example, withdrawal of beta blockers can precipitate an effect of myocardial infarction. Withdrawal of phenytoin can precipitate status epilepticus.
- Teratogenic effect: This refers to the ability of the drug to cause congenital abnormality in the fetus when given during pregnancy, for Example. cleft palate following the use of corticosteroids.
- Drug-induced disease or iatrogenic diseases: When certain drugs are used chronologically, they can produce disease, for Example. chronic use of aspirin can lead to the production of peptic ulcers.
Question 5. Write Short Note On Psychological Dependence.
Answer:
Psychological Dependence
Psychological drug dependence is one of the types of drug dependence.
- Psychological dependence is an intense desire to continue taking the drug as a patient feels that his/her well-being depends on the drug.
- Psychological dependence may start as a liking for the drug effects and this can progress to compulsive drug use in some individuals.
- The intensity of psychological dependence may vary from desire to craving.
- Certain degrees of psychological dependence consist of all patterns of self-medication.

Leave a Reply