Composite Resins
Resins Composition: Resin matrix/binder, ground quartz, colloidal silica glasses/ceramics containing heavy metals, filler, coupling agents, and organosilanes.
BIS GMA (Bisphenol – a – Glycidyl methacrylate).
Classification of Composite Resins
Based on the mean particle size of the major filler

Read And Learn More: Basic Dental Materials Notes
Properties of Composite Restorative Material
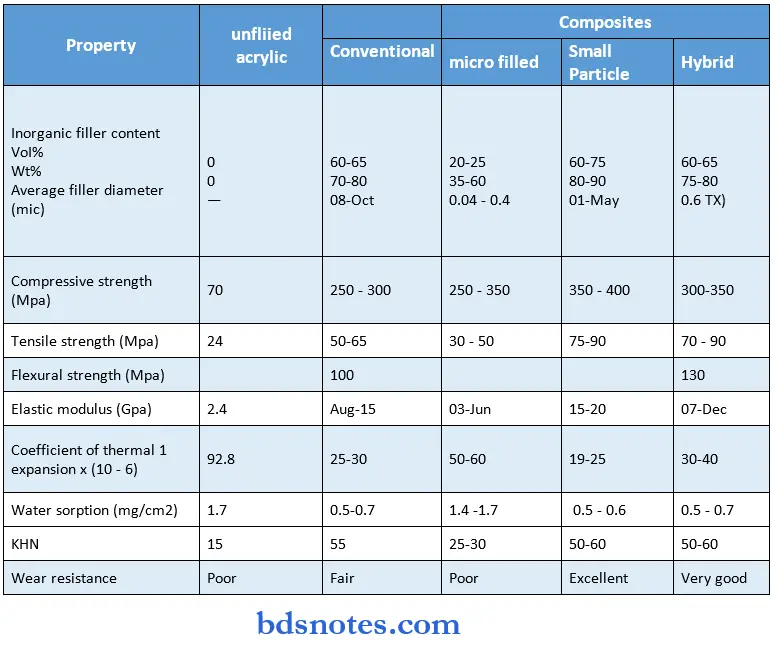
Other Important
Acid etch technique- The most effective way of improving the bond and marginal seal between the resin and enamel.
The most commonly used- is 37% phosphoric acid.
Dental Amalgam Composition
Mechanism of action – Creates micro porosities, increases surface area, and increases the surface energy of enamel.
Bonding Agents Enamel bonding agent – BISGMA / TEGDMA
Dentin bonding agents – 3 generations
- 1st Generation – Glycero- Phosphoric acid methacrylate
- 2nd Generation – Chloro substituted phosphate esters of various monomers –
- 3rd Generation – A primer is applied followed by the application of polymerizable monomers
- 4th Generation
- Prisma – NPG GMA and BPDM
- Resin adhesive (40% BIS GMA, 30 % VDMA, 30% – HEMA)
- HEMA – Hydroxy Ethyl Methacrylate
- EDTA- Ethylene Di Amine Tetra Acetic acid
- META – Methoxy Ethyl Trimellitic Acid
Bond Strength of Dentin Bonding Agent

Pit and Fissure Sealants
The most commonly and successfully used one is BIS – GMA resin
Dental Amalgam Composition
Resin Teeth Composition:
- Polymethyl methacrylate copolymerized with a cross-linking agent.
- High fractures toughness.
- Crazing if not cross-linked
- Dimensional change with water sorption
Porcelain teeth:
- Made with high fusing porcelains.
- Excellent biocompatibility
- The most suitable tooth-colored restorative material used to make denture teeth.
- Brittle, may chip
- Dimensionally stable
- Susceptible to crazing by thermal shock.
Dental Amalgam
Dental Amalgam Definition:
An amalgam is an alloy that contains mercury as one of its constituents.
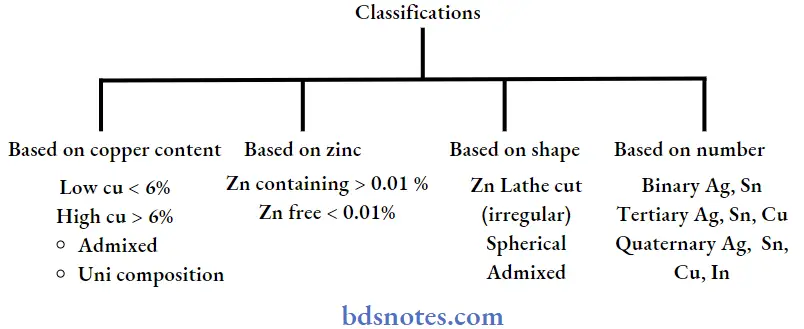
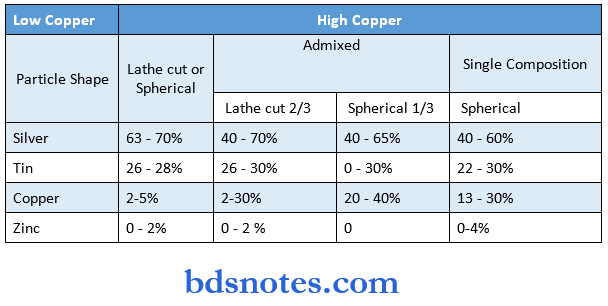
Dental Amalgam Composition:
Phases of amalgam
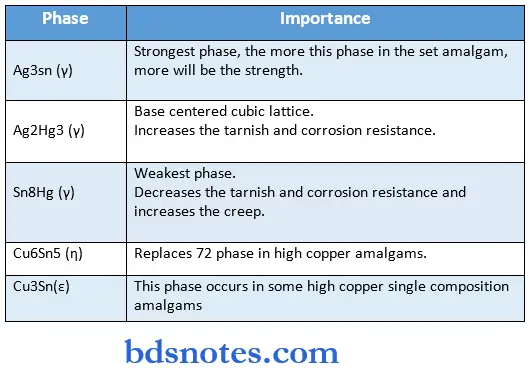
Unique Properties of Amalgam
- Microleakage
- Dimensional change
- Effect of moisture contamination
- Strength
- Creep
Dental Amalgam Composition
Dental Amalgam Manipulation
- Selection of material – Alloy, mercury
- Mercury: alloy ratio (Proportioning) -Eames technique – Hg: Alloy = 1:1
- Trituration
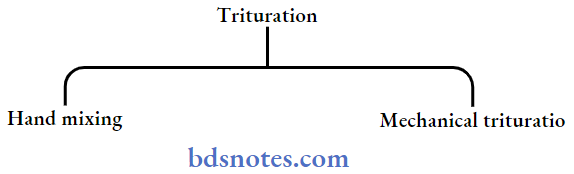
Dental Amalgam Purpose: To wet all the surfaces of alloy particles with mercury.
Under triturated mix- Rough grainy, compressive, and tensile strength decreases, Normal-Shining surface with smooth and soft consistency, greatest compressive and tensile strength and resistance to tarnishing and resistance.
Over triturated- Mix is soupy, working time decreases, and higher contraction of amalgam.
- Mulling
- Condensation
- Hand
- Mechanical
- Trimming and carving
- Burnishing
- Polishing
Advantages and disadvantages of dental amalgam
Dental Amalgam (ADA-1)[Spotter]
![Dental amalgam dental amalgam (ada-1) [spotter]](https://bdsnotes.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/Dental-amalgam-dental-amalgam-ada-1-spotter.png)
Dental Amalgam Composition Example:
- Ag, Sn, Cu
- Recommended by GV Black
- ADA Requires That Amalgam alloys be predominantly Ag and Sn
Uses: Permanent filing material in classes 1,2 and 2 5, where esthetics is not a prime consideration in taking dies in retrograde root canal filling restoration of the crown.
Dental Amalgam Composition
Dental casting alloys
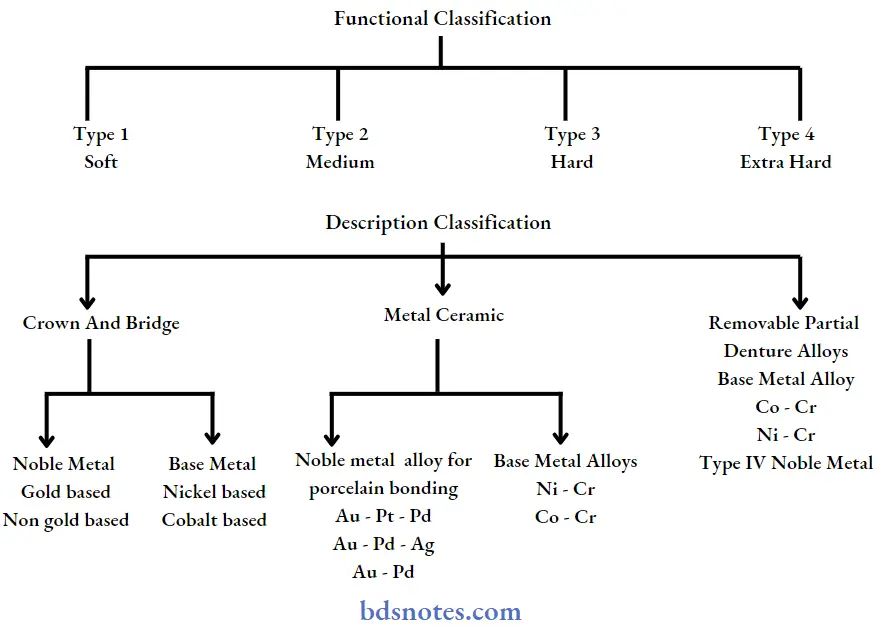
Dental casting alloys
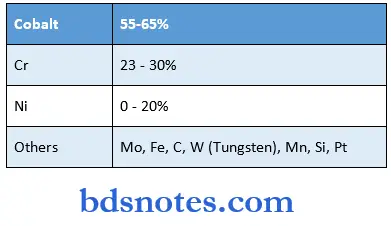
Cobalt chromium alloy (ADA 14) [Spotter]
- High strength excellent corrosion resistance
- Bright lustrous hard strong and non tarnishing qualities
Dental casting alloys Applications:
- Denture base
- Surgical Implants
Dental casting alloys Composition:
Gold Alloys
Classification and composition of gold Alloys
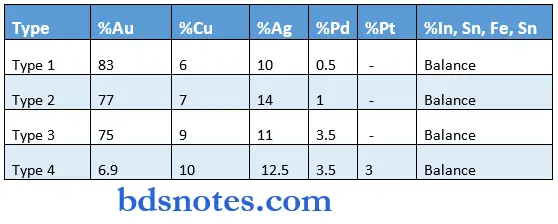
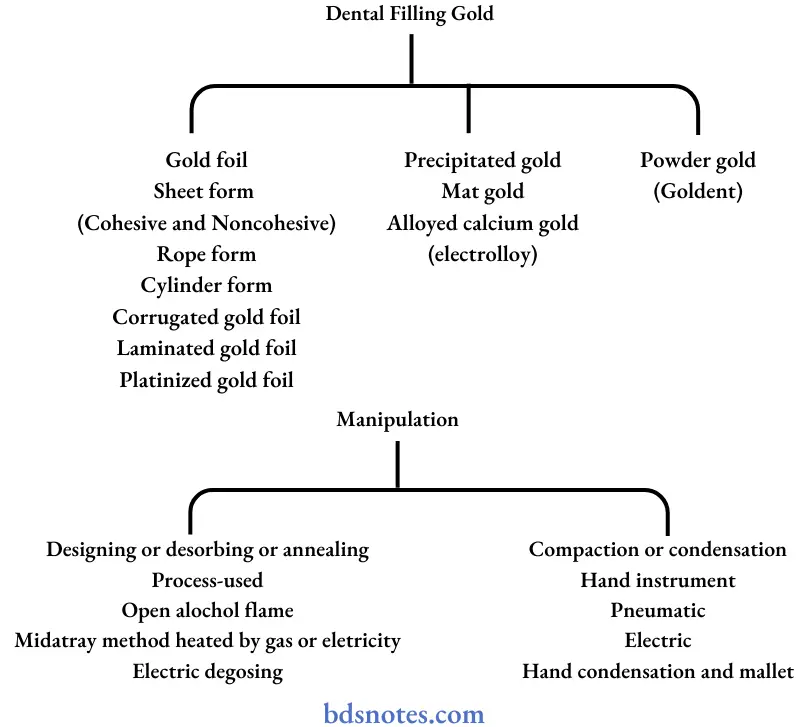
Direct filling gold
Gold Foil [Spotter] Applications:
- Pits and small class I restorations
- For repair of casting margins
- For class II & class V restorations
Dental Amalgam Composition
Gold Foil [Spotter] Thickness:
- No 4 – weight 4 gms, 0.51 um thick
- No 3 – weight 3 gms, 0.38 um thick
- Used in the manufacture of electrolytic and powder products.
Abrasive And Polishing Agents
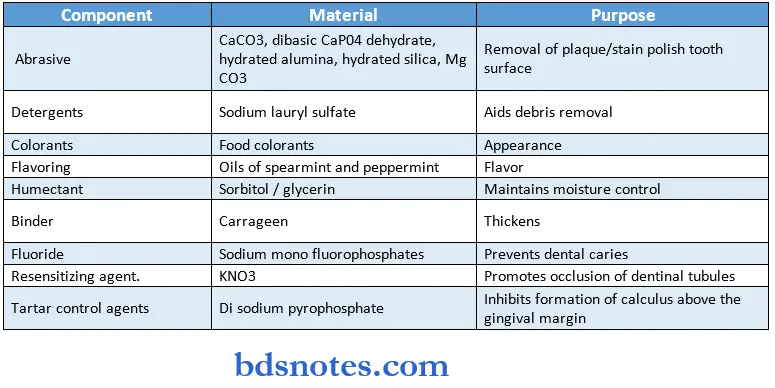
Typical Dentifrice Components
Pumice: [Spotter]
It is a highly siliceous material of volcanic origin and is suited for use either as an abrasive or polishing agent depending and particle size.
Pumice Uses:
- Smoothing dentures.
- Polishing teeth in the mouth
Leave a Reply